Interleukin-6: obstacles to targeting a complex cytokine in critical illness
- PMID: 33872590
- PMCID: PMC8051931
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00103-X
Interleukin-6: obstacles to targeting a complex cytokine in critical illness
Abstract
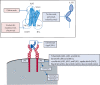
Circulating concentrations of the pleiotropic cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) are known to be increased in pro-inflammatory critical care syndromes, such as sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Elevations in serum IL-6 concentrations in patients with severe COVID-19 have led to renewed interest in the cytokine as a therapeutic target. However, although the pro-inflammatory properties of IL-6 are widely known, the cytokine also has a series of important physiological and anti-inflammatory functions. An adequate understanding of the complex processes by which IL-6 signalling occurs is crucial for the correct interpretation of IL-6 concentrations in the blood or lung, the use of IL-6 as a critical care biomarker, or the design of effective anti-IL-6 strategies. Here, we outline the role of IL-6 in health and disease, explain the different types of IL-6 signalling and their contribution to the net biological effect of the cytokine, describe the approaches to IL-6 inhibition that are currently available, and discuss implications for the future use of treatments such as tocilizumab in the critical care setting.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests SR-J has acted as a consultant and speaker for AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Chugai, Roche, Genentech Roche, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Sanofi; he is a co-owner of Conaris Research Institute, and an inventor on a patent for the sgp130Fc protein olamkicept now owned by Conaris Research Institute (PCT/EP2008/008736). NGM reports grant funding unrelated to the current work from Chiesi, Grifols, and pH Pharma; he has been an investigator and served on advisory boards for Chiesi, CSL Behring, Grifols, pH Pharma, and Vertex. OJM and GFC declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hirano T, Yasukawa K, Harada H, et al. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986;324:73–76. - PubMed
-
- Garbers C, Heink S, Korn T, Rose-John S. Interleukin-6: designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17:395–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

