Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Results From the CREDENCE Trial and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33874750
- PMCID: PMC8078131
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031623
Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Results From the CREDENCE Trial and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Chronic kidney disease with reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate or elevated albuminuria increases risk for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. This study assessed the effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) on stroke and atrial fibrillation/flutter (AF/AFL) from CREDENCE (Canagliflozin and Renal Events in Diabetes With Established Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation) and a meta-analysis of large cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs) of SGLT2i in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: CREDENCE randomized 4401 participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease to canagliflozin or placebo. Post hoc, we estimated effects on fatal or nonfatal stroke, stroke subtypes, and intermediate markers of stroke risk including AF/AFL. Stroke and AF/AFL data from 3 other completed large CVOTs and CREDENCE were pooled using random-effects meta-analysis.
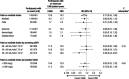
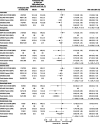
Results: In CREDENCE, 142 participants experienced a stroke during follow-up (10.9/1000 patient-years with canagliflozin, 14.2/1000 patient-years with placebo; hazard ratio [HR], 0.77 [95% CI, 0.55-1.08]). Effects by stroke subtypes were: ischemic (HR, 0.88 [95% CI, 0.61-1.28]; n=111), hemorrhagic (HR, 0.50 [95% CI, 0.19-1.32]; n=18), and undetermined (HR, 0.54 [95% CI, 0.20-1.46]; n=17). There was no clear effect on AF/AFL (HR, 0.76 [95% CI, 0.53-1.10]; n=115). The overall effects in the 4 CVOTs combined were: total stroke (HRpooled, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.82-1.12]), ischemic stroke (HRpooled, 1.01 [95% CI, 0.89-1.14]), hemorrhagic stroke (HRpooled, 0.50 [95% CI, 0.30-0.83]), undetermined stroke (HRpooled, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.49-1.51]), and AF/AFL (HRpooled, 0.81 [95% CI, 0.71-0.93]). There was evidence that SGLT2i effects on total stroke varied by baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (P=0.01), with protection in the lowest estimated glomerular filtration rate (<45 mL/min/1.73 m2]) subgroup (HRpooled, 0.50 [95% CI, 0.31-0.79]).
Conclusions: Although we found no clear effect of SGLT2i on total stroke in CREDENCE or across trials combined, there was some evidence of benefit in preventing hemorrhagic stroke and AF/AFL, as well as total stroke for those with lowest estimated glomerular filtration rate. Future research should focus on confirming these data and exploring potential mechanisms. Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT02065791.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; canagliflozin; glomerular filtration rate; hemorrhagic stroke; ischemic stroke.
Figures


Comment in
-
Treating Diabetes to Prevent Stroke.Stroke. 2021 May;52(5):1557-1560. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032725. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 33874746 No abstract available.
References
-
- Toyoda K, Ninomiya T. Stroke and cerebrovascular diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:823–833. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70026-2 - PubMed
-
- Mahmoodi BK, Yatsuya H, Matsushita K, Sang Y, Gottesman RF, Astor BC, Woodward M, Longstreth WT, Jr, Psaty BM, Shlipak MG, et al. Association of kidney disease measures with ischemic versus hemorrhagic strokes: pooled analyses of 4 prospective community-based cohorts. Stroke. 2014;45:1925–1931. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.004900 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ghoshal S, Freedman BI. Mechanisms of stroke in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2019;50:229–239. doi: 10.1159/000502446 - PubMed
-
- Bilha SC, Burlacu A, Siriopol D, Voroneanu L, Covic A. Primary prevention of stroke in chronic kidney disease patients: a scientific update. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;45:33–41. doi: 10.1159/000486016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

