The Visually Induced Motion Sickness Susceptibility Questionnaire (VIMSSQ): Estimating Individual Susceptibility to Motion Sickness-Like Symptoms When Using Visual Devices
- PMID: 33874752
- PMCID: PMC9846380
- DOI: 10.1177/00187208211008687
The Visually Induced Motion Sickness Susceptibility Questionnaire (VIMSSQ): Estimating Individual Susceptibility to Motion Sickness-Like Symptoms When Using Visual Devices
Abstract
Objective: Two studies were conducted to develop and validate a questionnaire to estimate individual susceptibility to visually induced motion sickness (VIMS).
Background: VIMS is a common side-effect when watching dynamic visual content from various sources, such as virtual reality, movie theaters, or smartphones. A reliable questionnaire predicting individual susceptibility to VIMS is currently missing. The aim was to fill this gap by introducing the Visually Induced Motion Sickness Susceptibility Questionnaire (VIMSSQ).
Methods: A survey and an experimental study were conducted. Survey: The VIMSSQ investigated the frequency of nausea, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and eyestrain when using different visual devices. Data were collected from a survey of 322 participants for the VIMSSQ and other related phenomena such as migraine. Experimental study: 23 participants were exposed to a VIMS-inducing visual stimulus. Participants filled out the VIMSSQ together with other questionnaires and rated their level of VIMS using the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ).
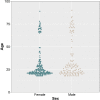
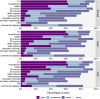
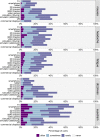
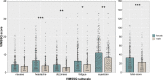
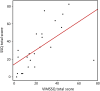
Results: Survey: The most prominent symptom when using visual devices was eyestrain, and females reported more VIMS than males. A one-factor solution with good scale reliability was found for the VIMSSQ. Experimental study: Regression analyses suggested that the VIMSSQ can be useful in predicting VIMS (R2 = .34) as measured by the SSQ, particularly when combined with questions pertaining to the tendency to avoid visual displays and experience syncope (R2 = .59).
Conclusion: We generated normative data for the VIMSSQ and demonstrated its validity.
Application: The VIMSSQ can become a valuable tool to estimate one's susceptibility to VIMS based on self-reports.
Keywords: cybersickness; migraine; sex; simulator sickness; virtual reality.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

