Complete genome sequence analysis of the peanut pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain Rs-P.362200
- PMID: 33874906
- PMCID: PMC8056632
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-021-02157-7
Complete genome sequence analysis of the peanut pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain Rs-P.362200
Abstract
Background: Bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum species complex is an important soil-borne disease worldwide that affects more than 450 plant species, including peanut, leading to great yield and quality losses. However, there are no effective measures to control bacterial wilt. The reason is the lack of research on the pathogenic mechanism of bacterial wilt.
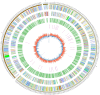
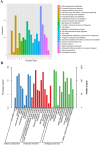
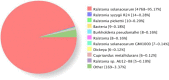
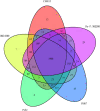
Results: Here, we report the complete genome of a toxic Ralstonia solanacearum species complex strain, Rs-P.362200, a peanut pathogen, with a total genome size of 5.86 Mb, encoding 5056 genes and the average G + C content of 67%. Among the coding genes, 75 type III effector proteins and 12 pseudogenes were predicted. Phylogenetic analysis of 41 strains including Rs-P.362200 shows that genetic distance mainly depended on geographic origins then phylotypes and host species, which associated with the complexity of the strain. The distribution and numbers of effectors and other virulence factors changed among different strains. Comparative genomic analysis showed that 29 families of 113 genes were unique to this strain compared with the other four pathogenic strains. Through the analysis of specific genes, two homologous genes (gene ID: 2_657 and 3_83), encoding virulence protein (such as RipP1) may be associated with the host range of the Rs-P.362200 strain. It was found that the bacteria contained 30 pathogenicity islands and 6 prophages containing 378 genes, 7 effectors and 363 genes, 8 effectors, respectively, which may be related to the mechanism of horizontal gene transfer and pathogenicity evaluation. Although the hosts of HA4-1 and Rs-P.362200 strains are the same, they have specific genes to their own genomes. The number of genomic islands and prophages in HA4-1 genome is more than that in Rs-P.36220, indicating a rapid change of the bacterial wilt pathogens.
Conclusion: The complete genome sequence analysis of peanut bacterial wilt pathogen enhanced the information of R. solanacearum genome. This research lays a theoretical foundation for future research on the interaction between Ralstonia solanacearum and peanut.
Keywords: Effector; Genome; Pathogenicity island; Peanut; Prophage; Ralstonia solanacearum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum Strain PeaFJ1 Provides Insights Into Its Strong Virulence in Peanut Plants.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;13:830900. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.830900. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35273586 Free PMC article.
-
Genomes of three tomato pathogens within the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex reveal significant evolutionary divergence.BMC Genomics. 2010 Jun 15;11:379. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-379. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20550686 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of the sesame pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain SEPPX 05.Genes Genomics. 2018 Jun;40(6):657-668. doi: 10.1007/s13258-018-0667-3. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Genes Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29892946
-
Ralstonia solanacearum, a widespread bacterial plant pathogen in the post-genomic era.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Sep;14(7):651-62. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12038. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23718203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenomics of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex.Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2012;50:67-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173000. Epub 2012 May 1. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2012. PMID: 22559068 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative genomics and host range analysis of four Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum strains isolated from sunflower reveals genomic and phenotypic differences.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 19;25(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10087-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38373891 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum Strain PeaFJ1 Provides Insights Into Its Strong Virulence in Peanut Plants.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;13:830900. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.830900. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35273586 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive genome sequence analysis of the devastating tobacco bacterial phytopathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain FJ1003.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 22;13:966092. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.966092. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36072670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J, Feng J. Advances in research of genetic diversity and pathogenome of Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Sci Agric Sin. 2013;46(14):2902–2909. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.14.006. - DOI
-
- Zheng XA. A systemic screening of effectors in Ralstonia Solanacearum and virulence study of Rip25 in potato. Huazhong Agric Univ. 2018.
-
- Shan WW. Comparative genomics and host specificity analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum race 4 strain SD54. Shandong Norm Univ. 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

