The impact of frailty on survival in elderly intensive care patients with COVID-19: the COVIP study
- PMID: 33874987
- PMCID: PMC8054503
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03551-3
The impact of frailty on survival in elderly intensive care patients with COVID-19: the COVIP study
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has led highly developed healthcare systems to the brink of collapse due to the large numbers of patients being admitted into hospitals. One of the potential prognostic indicators in patients with COVID-19 is frailty. The degree of frailty could be used to assist both the triage into intensive care, and decisions regarding treatment limitations. Our study sought to determine the interaction of frailty and age in elderly COVID-19 ICU patients.
Methods: A prospective multicentre study of COVID-19 patients ≥ 70 years admitted to intensive care in 138 ICUs from 28 countries was conducted. The primary endpoint was 30-day mortality. Frailty was assessed using the clinical frailty scale. Additionally, comorbidities, management strategies and treatment limitations were recorded.
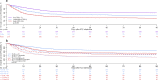
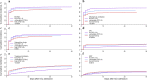
Results: The study included 1346 patients (28% female) with a median age of 75 years (IQR 72-78, range 70-96), 16.3% were older than 80 years, and 21% of the patients were frail. The overall survival at 30 days was 59% (95% CI 56-62), with 66% (63-69) in fit, 53% (47-61) in vulnerable and 41% (35-47) in frail patients (p < 0.001). In frail patients, there was no difference in 30-day survival between different age categories. Frailty was linked to an increased use of treatment limitations and less use of mechanical ventilation. In a model controlling for age, disease severity, sex, treatment limitations and comorbidities, frailty was independently associated with lower survival.
Conclusion: Frailty provides relevant prognostic information in elderly COVID-19 patients in addition to age and comorbidities. Trial registration Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04321265 , registered 19 March 2020.
Keywords: COVID-19; Elderly; Frailty; Outcome; Pandemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. JCS reports grants (full departmental disclosure) from Orion Pharma, Abbott Nutrition International, B. Braun Medical AG, CSEM AG, Edwards Lifesciences Services GmbH, Kenta Biotech Ltd, Maquet Critical Care AB, Omnicare Clinical Research AG, Nestle, Pierre Fabre Pharma AG, Pfizer, Bard Medica S.A., Abbott AG, Anandic Medical Systems, Pan Gas AG Healthcare, Bracco, Hamilton Medical AG, Fresenius Kabi, Getinge Group Maquet AG, Dräger AG, Teleflex Medical GmbH, Glaxo Smith Kline, Merck Sharp and Dohme AG, Eli Lilly and Company, Baxter, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, CSL Behring, Novartis, Covidien, Philips Medical, Phagenesis Ltd, Prolong Pharmaceuticals and Nycomed outside the submitted work. The money went into departmental funds. No personal financial gain applied.
Figures
Comment in
-
The impact of frailty on survival in elderly intensive care patients with COVID‑19: do not dismiss intensive care unit overcrowding.Crit Care. 2021 Jun 30;25(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03653-y. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34193242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Flaatten H, De Lange DW, Morandi A, Andersen FH, Artigas A, Bertolini G, Boumendil A, Cecconi M, Christensen S, Faraldi L, et al. The impact of frailty on ICU and 30-day mortality and the level of care in very elderly patients (>/= 80 years) Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(12):1820–1828. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4940-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guidet B, de Lange DW, Boumendil A, Leaver S, Watson X, Boulanger C, Szczeklik W, Artigas A, Morandi A, Andersen F, et al. The contribution of frailty, cognition, activity of daily life and comorbidities on outcome in acutely admitted patients over 80 years in European ICUs: the VIP2 study. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(1):57–69. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05853-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

