Lack of the peroxiredoxin 6 gene causes impaired spatial memory and abnormal synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 33874992
- PMCID: PMC8056661
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-021-00779-6
Lack of the peroxiredoxin 6 gene causes impaired spatial memory and abnormal synaptic plasticity
Abstract
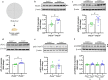
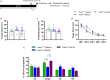
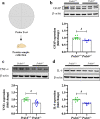
Peroxiredoxin 6 (PRDX6) is expressed dominantly in the astrocytes and exerts either neuroprotective or neurotoxic effects in the brain. Although PRDX6 can modulate several signaling cascades involving cognitive functions, its physiological role in spatial memory has not been investigated yet. This study aims to explore the function of the Prdx6 gene in spatial memory formation and synaptic plasticity. We first tested Prdx6-/- mice on a Morris water maze task and found that their memory performance was defective, along with reduced long-term potentiation (LTP) in CA3-CA1 hippocampal synapses recorded from hippocampal sections of home-caged mice. Surprisingly, after the probe test, these knockout mice exhibited elevated hippocampal LTP, higher phosphorylated ERK1/2 level, and decreased reactive astrocyte markers. We further reduced ERK1/2 phosphorylation by administering MEK inhibitor, U0126, into Prdx6-/- mice before the probe test, which reversed their spatial memory deficit. This study is the first one to report the role of PRDX6 in spatial memory and synaptic plasticity. Our results revealed that PRDX6 is necessary for maintaining spatial memory by modulating ERK1/2 phosphorylation and astrocyte activation.
Keywords: Long-term potentiation; Neuroinflammation; Peroxiredoxin 6; Reactive astrocyte; Spatial memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

