Emerging Roles of Coronavirus in Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 33875273
- PMCID: PMC8031002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.012
Emerging Roles of Coronavirus in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
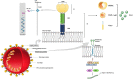
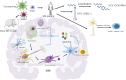
Virus infection can alter immune regulatory activity, and thus may be involved in the occurrence of autoimmune diseases. Recently, the pandemic of COVID-19 has posed a huge threat to public health and emerging evidence suggests that coronavirus may be implicated in the development and pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. However, how coronavirus infection impacts the risk of autoimmune disease remains largely unknown. In this review, we focused on the association between coronavirus and autoimmunity, and elucidated the molecular mechanisms linking coronavirus exposure to autoimmunity. Additionally, we briefly introduced the role that coronavirus plays in several autoimmune diseases including multiple sclerosis (MS), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and idiopathicthrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus, Autoimmune disease, Autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Utility of Serum S100B as A Marker in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients During and After the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic.Arch Med Res. 2022 Jul;53(5):543-544. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 25. Arch Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35637047 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to: Utility of Serum S100B as a Marker in SLE Patients During and After the SARS-Cov-2 Pandemic.Arch Med Res. 2022 Jul;53(5):545. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.05.005. Epub 2022 May 25. Arch Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35649743 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Lam CS, et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J Virol. 2012;86:3995–4008. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

