Improvement of the Bioavailability and Anti-hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis Effect of Albendazole-Isethionate/Hypromellose Acetate Succinate (HPMC-AS) Complex
- PMID: 33875425
- PMCID: PMC8218690
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02233-20
Improvement of the Bioavailability and Anti-hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis Effect of Albendazole-Isethionate/Hypromellose Acetate Succinate (HPMC-AS) Complex
Abstract
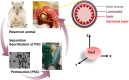
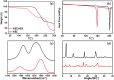
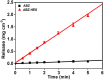
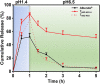
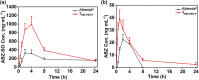
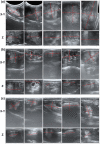
Maximizing the pharmacodynamics of albendazole (ABZ), which is used to treat echinococcoses, is essential for the long-term treatment of echinococcosis patients. ABZ is a weak base whose solubility depends on the pH value of the solvent. After it has been orally administered, its solubility drops sharply from when it is in gastric juices (pH 1.4) to when it is in intestinal juices (pH 6.5) and is subsequently absorbed in the ileum and jejunum. This results in low solubility and poor bioavailability of the drug. In this study, we developed an orally administered albendazole-isethionate (ABZ-HES)/hypromellose acetate succinate (HPMC-AS) complex tablet (TABZ-HES-H) with improved solubility and bioavailability. Previous studies demonstrated that ABZ-HES has a higher intrinsic dissolution rate under pH 1.4 than the ABZ free base used in the commercial product Albenda and that HPMC-AS can effectively inhibit ABZ crystallization, which could be due to the hydrophobic interaction between ABZ and HPMC-AS in an aqueous environment. In this study, the dissolution behavior of TABZ-HES-Hin vitro was studied by the two-step pH conversion method. Our results demonstrated that the oral bioavailability of TABZ-HES-H was approximately 2.6 times higher than that of ABZ. More importantly, in the rat model of secondary hepatic alveolar echinococcosis, the anti-hepatic alveolar echinococcosis effect of TABZ-HES-H was 3.4 times higher than that of a commercial product. The improved preparation with salt and polymer has proven to be a feasible method of improving the oral bioavailability and pharmacodynamics of ABZ.
Keywords: HPMC-AS; albendazole-isethionate; anti-hepatic alveolar echinococcosis effect; pharmacokinetics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metabolic mechanism and pharmacological study of albendazole in secondary hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (HAE) model rats.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 May 2;68(5):e0144923. doi: 10.1128/aac.01449-23. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38501660 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Oral Bioavailability and Anti-Echinococcosis Efficacy of Albendazole Achieved by Optimizing the "Spring" and "Parachute".Mol Pharm. 2019 Dec 2;16(12):4978-4986. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00851. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31613633
-
Supersaturated drug delivery system of albendazole salt-polymer complex for improving oral bioavailability and efficacy anti-secondary E. multilocularis.Acta Trop. 2024 Dec;260:107464. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2024.107464. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Acta Trop. 2024. PMID: 39536888
-
Therapeutic efficacy of nanocompounds in the treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcoses: challenges and future prospects.Parasitol Res. 2019 Sep;118(9):2455-2466. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06416-5. Epub 2019 Aug 11. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 31402401 Review.
-
Nanoformulations of albendazole as effective anticancer and antiparasite agents.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 Oct;12(20):2555-2574. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0102. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28954575 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic mechanism and pharmacological study of albendazole in secondary hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (HAE) model rats.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 May 2;68(5):e0144923. doi: 10.1128/aac.01449-23. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38501660 Free PMC article.
-
Combining solubilization and controlled release strategies to prepare pH-sensitive solid dispersion loaded with albendazole: in vitro and in vivo studies.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Dec 20;11:1522856. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1522856. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39758610 Free PMC article.
-
Ubenimex combined with Albendazole for the treatment of Echinococcus multilocularis-induced alveolar echinococcosis in mice.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Mar 15;11:1320308. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1320308. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38585297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wen H, New RRC, Muhmut M, Wang JH, Wang YH, Zhang JH, Shao YM, Craig PS. 1996. Pharmacology and efficacy of liposome-entrapped albendazole in experimental secondary alveolar echinococcosis and effect of co-administration with cimetidine. Parasitology 113:111–121. 10.1017/S003118200006635X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

