Beyond Homeostasis: Potassium and Pathogenesis during Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 33875474
- PMCID: PMC8486168
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00766-20
Beyond Homeostasis: Potassium and Pathogenesis during Bacterial Infections
Abstract
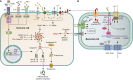
Potassium is an essential mineral nutrient required by all living cells for normal physiological function. Therefore, maintaining intracellular potassium homeostasis during bacterial infection is a requirement for the survival of both host and pathogen. However, pathogenic bacteria require potassium transport to fulfill nutritional and chemiosmotic requirements, and potassium has been shown to directly modulate virulence gene expression, antimicrobial resistance, and biofilm formation. Host cells also require potassium to maintain fundamental biological processes, such as renal function, muscle contraction, and neuronal transmission; however, potassium flux also contributes to critical immunological and antimicrobial processes, such as cytokine production and inflammasome activation. Here, we review the role and regulation of potassium transport and signaling during infection in both mammalian and bacterial cells and highlight the importance of potassium to the success and survival of each organism.
Keywords: host-pathogen interactions; potassium.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

