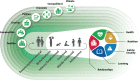
The principles of Nurturing Care promote human capital and mitigate adversities from preconception through adolescence
- PMID: 33875519
- PMCID: PMC8057542
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004436
The principles of Nurturing Care promote human capital and mitigate adversities from preconception through adolescence
Abstract
A comprehensive evidence-based framework is needed to guide policies and programmes that enable children and adolescents to accrue the human capital required to meet the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This paper proposes a comprehensive, multisectoral, multilevel life-course conceptualisation of human capital development by building on the Nurturing Care Framework (NCF), originally developed for the foundational period of growth and development through the age 3 years. Nurturing care (NC) comprises stable environments that promote children's health and nutrition, protect from threats, and provide opportunities for learning and responsive, emotionally supportive and developmentally enriching relationships. NC is fostered by families, communities, services, national policies and beyond. The principles apply across the life course, endorse equity and human rights, and promote long-term human capital. This paper presents an evidence-based argument for the extension of the NCF from preconception through adolescence (0-20 years), organised into six developmental periods: preconception/prenatal, newborn/birth, infancy/toddlerhood, preschool, middle childhood and adolescence. The proposed framework advances human capital within each developmental period by promoting resilience and adaptive developmental trajectories while mitigating negative consequences of adversities.Attaining the SDGs depends on strengthening human capital formation, extending throughout childhood and adolescence and supported by NC. Embedded in enabling laws, policies and services, the dynamic NCF components can mitigate adversities, enhance resilience and promote the well-being of marginalised groups. The life-course extension of the NCF is strategically positioned to enhance human capital, to attain the SDGs and to ensure that children or adolescents are not left behind in reaching their developmental potential.
Keywords: child health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Beyond pledges: academic journals in high-income countries can do more to decolonise global health.BMJ Glob Health. 2021 May;6(5):e006200. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-006200. BMJ Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34031135 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim JY. The human capital gap: getting governments to invest in people. Foreign Aff 2018;97:92.
-
- Bronfenbrenner U, Morris PA. The bioecological model of human development. In: Handbook of child psychology, 2007: 1–77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical