Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase, age, and immune activation in people living with HIV
- PMID: 33875612
- PMCID: PMC8319090
- DOI: 10.1136/jim-2021-001794
Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase, age, and immune activation in people living with HIV
Abstract
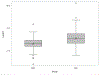
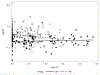
Immune activation complicates HIV despite antiretroviral therapy (ART). Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) catabolizes tryptophan (T) to kynurenine (K), regulating immune activity, and IDO activity increases with age. This study examines the relationship of IDO activity, bacterial translocation, and aging in people living with HIV (PLWH) on ART. Samples and data from PLWH on ART from the Centers for AIDS Research Network of Integrated Clinical Systems and from matched HIV-uninfected patients (controls) from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study and the Women's Interagency HIV Study were analyzed. The ratio of K to T (K:T) and neopterin were indicators of inflammation; 16S ribosomal DNA (16S rDNA) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were markers of bacterial translocation. Samples and data from 205 PLWH and 99 controls were analyzed. PLWH had higher K:T values across all ages, with a significant relationship between age and K:T for both groups. CD4 count or CD4 nadir had no association with K:T. There was no positive association between level of 16S rDNA or LPS detection and K:T. K:T and neopterin were associated. PLWH had elevated IDO activity, at younger ages, despite ART. This study suggests K:T ratio increases with age in both groups and is elevated in PLWH at all ages compared with age-matched controls.
Keywords: aging; immune tolerance; inflammation.
© American Federation for Medical Research 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SB is an Editorial Board Member of the Journal of Investigative Medicine. ALM is a shareholder in NewLink Genetics and receives licensing income from this source. All other authors declare no conflicts.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI103267/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI164078/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI154078/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

