Global dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 clades and their relation to COVID-19 epidemiology
- PMID: 33875719
- PMCID: PMC8055906
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-87713-x
Global dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 clades and their relation to COVID-19 epidemiology
Abstract
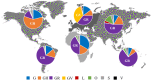
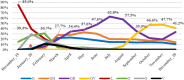
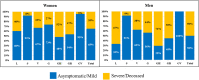
Expansion of COVID-19 worldwide increases interest in unraveling genomic variations of novel SARS-CoV-2 virus. Metadata of 408,493 SARS-CoV-2 genomes submitted to GISAID database were analyzed with respect to genomic clades and their geographic, age, and gender distributions. Of the currently known SARS-CoV-2 clades, clade GR was the most prevalent worldwide followed by GV then GH. Chronological analysis revealed expansion in SARS-CoV-2 clades carrying D614G mutations with the predominance of the newest clade, GV, in the last three months. D614G clades prevail in countries with more COVID-19 cases. Of them, the clades GH and GR were more frequently recovered from severe or deceased COVID-19 cases. In contrast, G and GV clades showed a significantly higher prevalence among asymptomatic patients or those with mild disease. Metadata analysis showed higher (p < 0.05) prevalence of severe/deceased cases among males than females and predominance of GR clade in female patients. Furthermore, severe disease/death was more prevalent (p < 0.05) in elderly than in adults/children. Higher prevalence of the GV clade in children compared to other age groups was also evident. These findings uniquely provide a statistical evidence on the adaptation-driven evolution of SARS-CoV-2 leading to altered infectivity, virulence, and mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: The species and its viruses—a statement of the coronavirus study group. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.07.937862. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV): Situation Report, 22. World Health Organization; 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

