Mechanisms of synaptic transmission dysregulation in the prefrontal cortex: pathophysiological implications
- PMID: 33875802
- PMCID: PMC8523584
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-021-01092-3
Mechanisms of synaptic transmission dysregulation in the prefrontal cortex: pathophysiological implications
Abstract
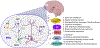
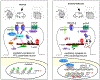
The prefrontal cortex (PFC) serves as the chief executive officer of the brain, controlling the highest level cognitive and emotional processes. Its local circuits among glutamatergic principal neurons and GABAergic interneurons, as well as its long-range connections with other brain regions, have been functionally linked to specific behaviors, ranging from working memory to reward seeking. The efficacy of synaptic signaling in the PFC network is profundedly influenced by monoaminergic inputs via the activation of dopamine, adrenergic, or serotonin receptors. Stress hormones and neuropeptides also exert complex effects on the synaptic structure and function of PFC neurons. Dysregulation of PFC synaptic transmission is strongly linked to social deficits, affective disturbance, and memory loss in brain disorders, including autism, schizophrenia, depression, and Alzheimer's disease. Critical neural circuits, biological pathways, and molecular players that go awry in these mental illnesses have been revealed by integrated electrophysiological, optogenetic, biochemical, and transcriptomic studies of PFC. Novel epigenetic mechanism-based strategies are proposed as potential avenues of therapeutic intervention for PFC-involved diseases. This review provides an overview of PFC network organization and synaptic modulation, as well as the mechanisms linking PFC dysfunction to the pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental, neuropsychiatric, and neurodegenerative diseases. Insights from the preclinical studies offer the potential for discovering new medical treatments for human patients with these brain disorders.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

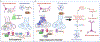
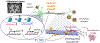
References
-
- Bourgeois JP, Goldman-Rakic PS & Rakic P Synaptogenesis in the prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkeys. Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 4, 78–96 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Fuster JM & Alexander GE Neuron activity related to short-term memory. Science 173, 652–654 (1971). - PubMed
-
- Goldman-Rakic PS Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron 14, 477–485 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

