Artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging to combat coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a detailed review with direction for future research
- PMID: 33875900
- PMCID: PMC8047522
- DOI: 10.1007/s10462-021-09985-z
Artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging to combat coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a detailed review with direction for future research
Abstract
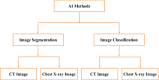
Since early 2020, the whole world has been facing the deadly and highly contagious disease named coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the World Health Organization declared the pandemic on 11 March 2020. Over 23 million positive cases of COVID-19 have been reported till late August 2020. Medical images such as chest X-rays and Computed Tomography scans are becoming one of the main leading clinical diagnosis tools in fighting against COVID-19, underpinned by Artificial Intelligence based techniques, resulting in rapid decision-making in saving lives. This article provides an extensive review of AI-based methods to assist medical practitioners with comprehensive knowledge of the efficient AI-based methods for efficient COVID-19 diagnosis. Nearly all the reported methods so far along with their pros and cons as well as recommendations for improvements are discussed, including image acquisition, segmentation, classification, and follow-up diagnosis phases developed between 2019 and 2020. AI and machine learning technologies have boosted the accuracy of Covid-19 diagnosis, and most of the widely used deep learning methods have been implemented and worked well with a small amount of data for COVID-19 diagnosis. This review presents a detailed mythological analysis for the evaluation of AI-based methods used in the process of detecting COVID-19 from medical images. However, due to the quick outbreak of Covid-19, there are not many ground-truth datasets available for the communities. It is necessary to combine clinical experts' observations and information from images to have a reliable and efficient COVID-19 diagnosis. This paper suggests that future research may focus on multi-modality based models as well as how to select the best model architecture where AI can introduce more intelligence to medical systems to capture the characteristics of diseases by learning from multi-modality data to obtain reliable results for COVID-19 diagnosis for timely treatment .
Keywords: Artificial intelligence(AI); Classification; Coronavirus (COVID-19); Deep learning; Medical imaging; Segmentation.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2021.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning: A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(12):1403-1418. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210713113439. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34259149 Review.
-
A Promising and Challenging Approach: Radiologists' Perspective on Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Fighting COVID-19.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Oct 18;11(10):1924. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11101924. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combating COVID-19 Crisis using Artificial Intelligence (AI) Based Approach: Systematic Review.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(8):737-753. doi: 10.2174/0115680266282179240124072121. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38318824
-
Systematic review of artificial intelligence techniques in the detection and classification of COVID-19 medical images in terms of evaluation and benchmarking: Taxonomy analysis, challenges, future solutions and methodological aspects.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Oct;13(10):1381-1396. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.028. Epub 2020 Jul 1. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32646771 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on the Use of AI and ML for Fighting the COVID-19 Pandemic.IEEE Trans Artif Intell. 2021 Mar 1;1(3):258-270. doi: 10.1109/TAI.2021.3062771. eCollection 2020 Dec. IEEE Trans Artif Intell. 2021. PMID: 35784006 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Deep Learning Model for the Diagnosis and Discrimination of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Pneumonia for Children Using Chest Radiography Images and Clinical Information.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jun 24;16:4083-4092. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S404786. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37388188 Free PMC article.
-
A medical multimodal large language model for future pandemics.NPJ Digit Med. 2023 Dec 2;6(1):226. doi: 10.1038/s41746-023-00952-2. NPJ Digit Med. 2023. PMID: 38042919 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Survey of Using Machine Learning in the COVID-19 Pandemic.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;11(7):1155. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071155. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multimodal multidomain multilingual medical foundation model for zero shot clinical diagnosis.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 Feb 6;8(1):86. doi: 10.1038/s41746-024-01339-7. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 39915635 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 26;13:845305. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.845305. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35559010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achilles F, Ichim A. E, Coskun H, Tombari F, Noachtar S, Navab N (2016) Patient MoCap: Human pose estimation under blanket occlusion for hospital monitoring applications. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention pp. 491–499
-
- Afshar P, Heidarian S, Naderkhani F, et al (2020) Covid-caps: A capsule network-based framework for identification of covid-19 cases from x-ray images. arXiv:2004.02696 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alom M.Z, Rahman M.M.S, Nasrin M.S, Taha T.M, Asari V.K (2020) Covid MTNet: Covid-19 detection with multi-task deep learning approaches. arXiv:2004.03747
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
