Hyperphosphorylation of Human Osteopontin and Its Impact on Structural Dynamics and Molecular Recognition
- PMID: 33876640
- PMCID: PMC8154273
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00050
Hyperphosphorylation of Human Osteopontin and Its Impact on Structural Dynamics and Molecular Recognition
Abstract
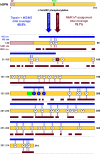
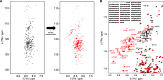
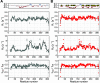
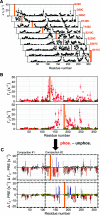
Protein phosphorylation is an abundant post-translational modification (PTM) and an essential modulator of protein functionality in living cells. Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) are particular targets of PTM protein kinases due to their involvement in fundamental protein interaction networks. Despite their dynamic nature, IDPs are far from having random-coil conformations but exhibit significant structural heterogeneity. Changes in the molecular environment, most prominently in the form of PTM via phosphorylation, can modulate these structural features. Therefore, how phosphorylation events can alter conformational ensembles of IDPs and their interactions with binding partners is of great interest. Here we study the effects of hyperphosphorylation on the IDP osteopontin (OPN), an extracellular target of the Fam20C kinase. We report a full characterization of the phosphorylation sites of OPN using a combined nuclear magnetic resonance/mass spectrometry approach and provide evidence for an increase in the local flexibility of highly phosphorylated regions and the ensuing overall structural elongation. Our study emphasizes the simultaneous importance of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions in the formation of compact substates in IDPs and their relevance for molecular recognition events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cooperative unfolding of compact conformations of the intrinsically disordered protein osteopontin.Biochemistry. 2013 Aug 6;52(31):5167-75. doi: 10.1021/bi400502c. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23848319 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Correlated Segment Fluctuations in IDPs upon Complex Formation as an Allosteric Regulatory Mechanism.J Mol Biol. 2018 Aug 3;430(16):2439-2452. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.04.035. Epub 2018 May 5. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29733855
-
How multisite phosphorylation impacts the conformations of intrinsically disordered proteins.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 May 4;17(5):e1008939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008939. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33945530 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Function by Post-translational Modifications.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):6696-705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.695056. Epub 2016 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26851279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Features of molecular recognition of intrinsically disordered proteins via coupled folding and binding.Protein Sci. 2019 Nov;28(11):1952-1965. doi: 10.1002/pro.3718. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 31441158 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Osteopontin: A Bone-Derived Protein Involved in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis Immunopathology.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 9;13(3):502. doi: 10.3390/biom13030502. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular basis for cellular function of intrinsically disordered protein regions.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Mar;25(3):187-211. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00673-0. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 37957331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Omics Profiling Identifies Microglial Annexin A2 as a Key Mediator of NF-κB Pro-inflammatory Signaling in Ischemic Reperfusion Injury.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024 Feb;23(2):100723. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100723. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38253182 Free PMC article.
-
Milk Osteopontin and Human Health.Nutrients. 2023 May 23;15(11):2423. doi: 10.3390/nu15112423. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanopore Stochastic Sensing Based on Non-covalent Interactions.Anal Chem. 2021 Aug 10;93(31):10974-10981. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02102. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34319076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin E. W.; Holehouse A. S.; Grace C. R.; Hughes A.; Pappu R. V.; Mittag T. (2016) Sequence Determinants of the Conformational Properties of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein Prior to and upon Multisite Phosphorylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 15323–15335. 10.1021/jacs.6b10272. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gibbs E. B.; Lu F.; Portz B.; Fisher M. J.; Medellin B. P.; Laremore T. N.; Zhang Y. J.; Gilmour D. S.; Showalter S. A. (2017) Phosphorylation Induces Sequence-Specific Conformational Switches in the RNA Polymerase II C-Terminal Domain. Nat. Commun. 8, 15233.10.1038/ncomms15233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

