Characteristics, complications, and sites of bleeding among infants and toddlers less than 2 years of age with VWD
- PMID: 33877293
- PMCID: PMC8095137
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004141
Characteristics, complications, and sites of bleeding among infants and toddlers less than 2 years of age with VWD
Abstract
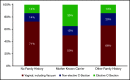
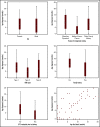
Data on infants and toddlers (ITs) with von Willebrand disease (VWD) are lacking. We used data collected in the US Hemophilia Treatment Center Network (USHTCN) to describe birth characteristics, bleeding episodes, and complications experienced by 105 patients with VWD who were <2 years of age. In 68% of the patients, the reason for diagnostic testing was a family history of a bleeding disorder. The mean age at diagnosis was 7 months, with little variation by sex. Patients with type 2 VWD were diagnosed earlier than those with types 1 or 3 (P = .04), and those with a family history were diagnosed ∼4 months earlier than those with none (P < .001). Among the patients who experienced a bleeding event (70%), oral mucosa was the most common site of the initial bleeding episode (32%), followed by circumcision-related (12%) and intracranial/extracranial bleeding (10%). Forty-one percent of the initial bleeding events occurred before 6 months of age, and 68% of them occurred before the age of 1 year. Approximately 5% of the cohort experienced an intracranial hemorrhage; however, none was associated with delivery at birth. Bleeding patterns and rates were similar by sex (P = .40) and VWD type (P = .10). Forty-seven percent were treated with plasma-derived von Willebrand factor VIII concentrates. The results of this study indicate that a high percentage of ITs diagnosed with VWD and receiving care within the multidisciplinary structure of the USHTCN have a family history of VWD. In addition, bleeding events such as circumcision-related, oropharyngeal, and intracranial or extracranial episodes are common and are leading indicators for treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cabrera ME, Artigas CG, Páez E, et al. Enfermedad de von Willebrand en la IX Region de Chile. [Von Willebrand’s disease in the IX Region of Chile]. Rev Med Chil. 1989;117(4):423-430. - PubMed
-
- Werner EJ, Broxson EH, Tucker EL, Giroux DS, Shults J, Abshire TC. Prevalence of von Willebrand disease in children: a multiethnic study. J Pediatr. 1993;123(6):893-898. - PubMed
-
- Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, Dini E. Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand’s disease. Blood. 1987;69(2):454-459. - PubMed
-
- Nitu-Whalley IC, Lee CA, Griffioen A, Jenkins PV, Pasi KJ. Type 1 von Willebrand disease - a clinical retrospective study of the diagnosis, the influence of the ABO blood group and the role of the bleeding history. Br J Haematol. 2000;108(2):259-264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

