Inhibiting autophagy targets human leukemic stem cells and hypoxic AML blasts by disrupting mitochondrial homeostasis
- PMID: 33877295
- PMCID: PMC8095145
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002666
Inhibiting autophagy targets human leukemic stem cells and hypoxic AML blasts by disrupting mitochondrial homeostasis
Abstract
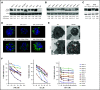
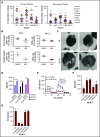
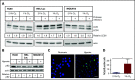
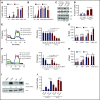
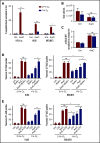
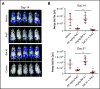
Leukemia stem cells (LSCs) and therapy-resistant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts contribute to the reinitiation of leukemia after remission, necessitating therapeutic interventions that target these populations. Autophagy is a prosurvival process that allows for cells to adapt to a variety of stressors. Blocking autophagy pharmacologically by using mechanistically distinct inhibitors induced apoptosis and prevented colony formation in primary human AML cells. The most effective inhibitor, bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1), also prevented the in vivo maintenance of AML LSCs in NSG mice. To understand why Baf A1 exerted the most dramatic effects on LSC survival, we evaluated mitochondrial function. Baf A1 reduced mitochondrial respiration and stabilized PTEN-induced kinase-1 (PINK-1), which initiates autophagy of mitochondria (mitophagy). Interestingly, with the autophagy inhibitor chloroquine, levels of enhanced cell death and reduced mitochondrial respiration phenocopied the effects of Baf A1 only when cultured in hypoxic conditions that mimic the marrow microenvironment (1% O2). This indicates that increased efficacy of autophagy inhibitors in inducing AML cell death can be achieved by concurrently inducing mitochondrial damage and mitophagy (pharmacologically or by hypoxic induction) and blocking mitochondrial degradation. In addition, prolonged exposure of AML cells to hypoxia induced autophagic flux and reduced chemosensitivity to cytarabine (Ara-C), which was reversed by autophagy inhibition. The combination of Ara-C with Baf A1 also decreased tumor burden in vivo. These findings demonstrate that autophagy is critical for mitochondrial homeostasis and survival of AML cells in hypoxia and support the development of autophagy inhibitors as novel therapeutic agents for AML.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SYK inhibition targets acute myeloid leukemia stem cells by blocking their oxidative metabolism.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 6;11(11):956. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03156-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33159047 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK-ULK1-Mediated Autophagy Confers Resistance to BET Inhibitor JQ1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 1;23(11):2781-2794. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1903. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27864418
-
Deciphering the mitophagy receptor network identifies a crucial role for OPTN (optineurin) in acute myeloid leukemia.Autophagy. 2023 Nov;19(11):2982-2996. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2230839. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 37439113 Free PMC article.
-
An updated outlook on autophagy mechanism and how it supports acute myeloid leukemia maintenance.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Nov;1879(6):189214. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189214. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39515545 Review.
-
Targeting mitochondrial respiration for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;182:114253. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114253. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33011159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between autophagy and metabolism: implications for cell survival in acute myeloid leukemia.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jan 24;10(1):46. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01823-9. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38267416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy a Close Relative of AML Biology.Biology (Basel). 2021 Jun 18;10(6):552. doi: 10.3390/biology10060552. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Unc51-like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1 (ULK1) Overcomes Adaptive Drug Resistance in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia.Mol Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 1;21(6):548-563. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-22-0343. Mol Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36787422 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of E2F Family in Cancer Stem Cells.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 12;11:723137. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.723137. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34476219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Induced Metabolic and Functional Changes in Oral CSCs: Implications for Stemness and Viability Modulation Through BNIP3-Driven Mitophagy.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Feb;29(3):e70400. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70400. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39945227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shlush LI, Mitchell A, Heisler L, et al. . Tracing the origins of relapse in acute myeloid leukaemia to stem cells. Nature. 2017;547(7661):104-108. - PubMed
-
- Hope KJ, Jin L, Dick JE. Acute myeloid leukemia originates from a hierarchy of leukemic stem cell classes that differ in self-renewal capacity. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(7):738-743. - PubMed
-
- Paietta E. Consensus on MRD in AML? Blood. 2018;131(12):1265-1266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

