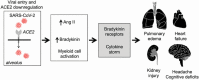
A Cytokine/Bradykinin Storm Comparison: What Is the Relationship Between Hypertension and COVID-19?
- PMID: 33877321
- PMCID: PMC8083217
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa217
A Cytokine/Bradykinin Storm Comparison: What Is the Relationship Between Hypertension and COVID-19?
Figures

References
-
- Buszko M, Park J, Verthelyi D, Sen R, Young HA, Rosenberg AS. The dynamic changes in cytokine responses in COVID-19: a snapshot of the current state of knowledge. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:1146–1151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

