Identifying lumbosacral plexus nerve root abnormalities in patients with sciatica using 3T readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion weighted MR neurography
- PMID: 33877460
- PMCID: PMC8058120
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-021-00992-w
Identifying lumbosacral plexus nerve root abnormalities in patients with sciatica using 3T readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion weighted MR neurography
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the accuracy of Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) using the Readout Segmentation of Long Variable Echo-trains (RESOLVE) sequence in detecting lumbosacral nerve abnormalities.
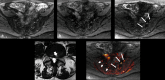
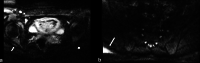
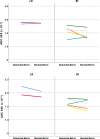
Methods: Following institutional ethics committee approval, patients with sciatica-type lower limb radicular symptoms (n = 110) were recruited and prospectively scanned using 3T MRI. Additional participants (n = 17) who underwent neurophysiological testing (EMG/NCV), were also prospectively studied. In addition to routine lumbar spine MRI, a DWI-RESOLVE sequence of the lumbosacral plexus was performed. Two radiologists, blinded to the side of patient symptoms, independently evaluated the MR images. The size and signal intensity changes of the nerves were evaluated using ordinal 4-point Likert-scales. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and size were measured for affected and normal nerves. Inter-observer agreement was determined with kappa statistics; κ.
Results: In patients who did not undergo EMG/NCV testing (n = 110), the DWI-RESOLVE sequence detected lumbosacral nerve abnormalities that correlated with symptoms in 36.3% (40/110). This is a similar percentage to patients who underwent EMG/NCV testing, which was positive and correlated with symptoms in 41.2% (7/17). Inter-observer agreement for evaluation of lumbosacral nerve abnormalities was excellent and ranged from 0.87 to 0.94. SNR and nerve size measurements demonstrated statistically significant differences for the L5 and S1 nerves (p value < 0.05) for patients who did not undergo EMG/NCV testing.
Conclusion: The DWI-RESOLVE sequence is a promising new method that may permit accurate detection and localization of lumbar nerve abnormalities in patients with sciatica.
Keywords: Evidence-based practice; Magnetic resonance imaging; Sciatica; Spine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

