An Overview on Recent Progress of Metal Oxide/Graphene/CNTs-Based Nanobiosensors
- PMID: 33877478
- PMCID: PMC8056378
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-021-03519-w
An Overview on Recent Progress of Metal Oxide/Graphene/CNTs-Based Nanobiosensors
Abstract
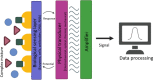
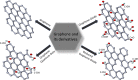
Nanobiosensors are convenient, practical, and sensitive analyzers that detect chemical and biological agents and convert the results into meaningful data between a biologically active molecule and a recognition element immobilized on the surface of the signal transducer by a physicochemical detector. Due to their fast, accurate and reliable operating characteristics, nanobiosensors are widely used in clinical and nonclinical applications, bedside testing, medical textile industry, environmental monitoring, food safety, etc. They play an important role in such critical applications. Therefore, the design of the biosensing interface is essential in determining the performance of the nanobiosensor. The unique chemical and physical properties of nanomaterials have paved the way for new and improved sensing devices in biosensors. The growing demand for devices with improved sensing and selectivity capability, short response time, lower limit of detection, and low cost causes novel investigations on nanobiomaterials to be used as biosensor scaffolds. Among all other nanomaterials, studies on developing nanobiosensors based on metal oxide nanostructures, graphene and its derivatives, carbon nanotubes, and the widespread use of these nanomaterials as a hybrid structure have recently attracted attention. Nanohybrid structures created by combining these nanostructures will directly meet the future biosensors' needs with their high electrocatalytic activities. This review addressed the recent developments on these nanomaterials and their derivatives, and their use as biosensor scaffolds. We reviewed these popular nanomaterials by evaluating them with comparative studies, tables, and charts.
Keywords: Carbon nanotubes; Graphene; Metal oxides; Nanobiosensors; Nanohybrids biosensor scaffolds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 5;21(4):1109. doi: 10.3390/s21041109. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobiosensors for detection of opioids: A review of latest advancements.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022 Oct;179:79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2022.08.017. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022. PMID: 36067954 Review.
-
Cancer diagnosis using nanomaterials based electrochemical nanobiosensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Feb 1;126:773-784. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.026. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 30554099 Review.
-
Graphene for Nanobiosensors and Nanobiochips.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1351:203-232. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4923-3_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35175618
-
Nanobiosensors: Concepts and Emerging Clinical Applications.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2024;12(3):197-205. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666230901160530. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37680159 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress on Green New Phase Extraction and Preparation of Polyphenols in Edible Oil.Molecules. 2023 Dec 18;28(24):8150. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248150. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psidium guajava mediated green synthesized cobalt oxide nanoparticles dispersed on reduced graphene oxide for electrocatalytic water splitting.RSC Adv. 2025 May 1;15(18):13786-13798. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00040h. eCollection 2025 Apr 28. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40313315 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Biopsy-Based Biosensors for MRD Detection and Treatment Monitoring in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 15;11(10):394. doi: 10.3390/bios11100394. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34677350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: An overview on possible transmission ways, sampling matrices and diagnosis.Bioimpacts. 2024;14(6):29968. doi: 10.34172/bi.2024.29968. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 39493896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid assays of SARS-CoV-2 virus and noble biosensors by nanomaterials.Nano Converg. 2024 Jan 8;11(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40580-023-00408-z. Nano Converg. 2024. PMID: 38190075 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clark L, Lyons C (1962) Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 102(29):29–45 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

