Emerging Role of PD-1 in the Central Nervous System and Brain Diseases
- PMID: 33877518
- PMCID: PMC8353059
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-021-00683-y
Emerging Role of PD-1 in the Central Nervous System and Brain Diseases
Abstract
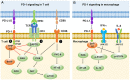
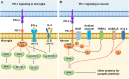
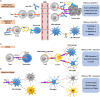
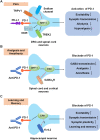
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is an immune checkpoint modulator and a major target of immunotherapy as anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in cancer treatment. Accumulating evidence suggests an important role of PD-1 in the central nervous system (CNS). PD-1 has been implicated in CNS disorders such as brain tumors, Alzheimer's disease, ischemic stroke, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, cognitive function, and pain. PD-1 signaling suppresses the CNS immune response via resident microglia and infiltrating peripheral immune cells. Notably, PD-1 is also widely expressed in neurons and suppresses neuronal activity via downstream Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 and modulation of ion channel function. An improved understanding of PD-1 signaling in the cross-talk between glial cells, neurons, and peripheral immune cells in the CNS will shed light on immunomodulation, neuromodulation, and novel strategies for treating brain diseases.
Keywords: Central nervous system; Immune checkpoint; Immunotherapy; Neurotherapy; PD-1.
© 2021. Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, CAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

