Lenvatinib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): a retrospective controlled study
- PMID: 33877527
- PMCID: PMC8286947
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10184-9
Lenvatinib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): a retrospective controlled study
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the efficacy and safety of combined treatment with lenvatinib and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) versus TACE only in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC).
Methods: Of the 120 patients enrolled in this study, 60 patients received treatment with TACE only, and 60 patients received TACE plus lenvatinib. We retrospectively compared the clinical outcomes including overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and tumor response between the two groups. Both PFS and tumor response were based on the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST). Adverse events were analyzed to assess the safety profiles.
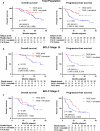
Results: The 1-year and 2-year OS rates were significantly higher in the TACE + lenvatinib group (88.4% and 79.8%) than that in the TACE group (79.2% and 49.2%, p = 0.047). A similar PFS benefit was observed in the TACE + lenvatinib group (1-y PFS rate: 78.4% vs. 64.7%, 2-y PFS rate: 45.5% vs. 38.0%, p < 0.001). The best overall objective response rate (ORR) was also better with TACE + lenvatinib treatment (ORR: 68.3% vs. 31.7%, p < 0.001) and disease control rate (DCR) numerically increased in the TACE + lenvatinib treatment (93.3% vs. 86.7%, p = 0.224). Patients' liver function remained comparable to baseline in the TACE + lenvatinib group. The most common adverse events were decreased albumin (55.0%), hypertension (48.3%) and decreased platelet count (46.7%) in the TACE + lenvatinib group.
Conclusions: Combination treatment with TACE and lenvatinib may significantly improve clinical outcomes over TACE monotherapy with a manageable safety profile for unresectable HCC. The efficacy of the combination treatment should be validated in prospective studies with a large sample size.
Keywords: Adverse events; Combination therapy; Lenvatinib; Liver function; Monotherapy; Overall survival; Progression-free survival; Transarterial chemoembolization; Tumor response; Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Zhigang Fu, Xiaowei Li, Jiaming Zhong, Xiaoxia Chen, Kunkun Cao, Ning Ding, Li Liu, Xiaoli Zhang, Jian Zhai and Zengqiang Qu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

