Successful treatment of vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT)
- PMID: 33877735
- PMCID: PMC8362082
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.15346
Successful treatment of vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT)
Abstract
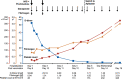
Cases of unusual thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after administration of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AstraZeneca) have been reported. The term vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) was coined to reflect this new phenomenon. In vitro experiments with VIPIT patient sera indicated that high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) competitively inhibit the platelet-activating properties of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine induced antibodies. Here, we report a case of a 62-year-old woman who had received this vaccine and developed VIPIT. She visited the emergency ward because of petechiae and hematomas. In the laboratory work-up, thrombocytopenia, low fibrinogen, elevated D-dimer, and positivity in the platelet factor 4/heparin-enzyme-immunoassay were present. Signs and symptoms of thrombosis were absent. Upon immediate therapy with non-heparin anticoagulation, high-dose IVIG, and prednisolone, laboratory parameters steadily improved and the patient was discharged from hospital without thrombotic complications. We conclude that early initiation of VIPIT treatment results in a swift response without thrombotic complications.
Keywords: COVID-19; ChAdOx1 vaccine; VIPIT; high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins; vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Successful treatment of vaccine-induced prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT): COMMENT from Roberge, et al.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Aug;19(8):2091-2092. doi: 10.1111/jth.15369. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34327827 No abstract available.
References
-
- Greinacher A, Thiele T, Warkentin TE, Weisser K, Kyrle P, Eichinger S. A prothrombotic thrombocytopenic disorder resembling heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia following Coronavirus‐19 vaccination. Research Square [Peprint] 28 Mar, 2021 [cited 4 Apr, 2021]. Avaiable from 10.21203/rs.3.rs-362354/v1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical