Serious adverse reactions associated with ivermectin: A systematic pharmacovigilance study in sub-Saharan Africa and in the rest of the World
- PMID: 33878105
- PMCID: PMC8087035
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009354
Serious adverse reactions associated with ivermectin: A systematic pharmacovigilance study in sub-Saharan Africa and in the rest of the World
Abstract
Background: Ivermectin is known to cause severe encephalopathies in subjects infected with loiasis, an endemic parasite in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). In addition, case reports have described ivermectin-related serious adverse drug reactions (sADRs) such as toxidermias, hepatic and renal disorders. The aim of this study was to identify suspected sADRs reported after ivermectin administration in VigiBase, the World Health Organization's global individual case safety reports database and analyze their frequency relative to the frequency of these events after other antinematodal drugs reported in SSA and other areas of the world (ROW).
Methods: All antinematodal-related sADRs were extracted from VigiBase. Disproportionality analyses were conducted to investigate nervous, cutaneous, psychiatric, respiratory, renal, hepatic and cardiac suspected sADRs reported after ivermectin and benzimidazole drug administration across the world, in SSA and RoW.
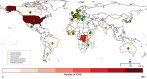
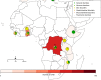
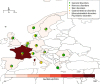
Principal findings: 2041 post-ivermectin or post-benzimidazole suspected sADRs were identified including 667 after ivermectin exposure (208 in SSA and 459 in the RoW). We found an increased reporting for toxidermias, encephalopathies, confusional disorders after ivermectin compared to benzimidazole drug administration. Encephalopathies were not only reported from SSA but also from the RoW (adjusted reporting odds ratios [aROR] 6.30, 95% confidence interval: 2.68-14.8), highlighting the fact these types of sADR occur outside loiasis endemic regions.
Conclusion: We described for the first time suspected sADRs associated with ivermectin exposure according to geographical origin. While our results do not put in question ivermectin's excellent safety profile, they show that as for all drugs, appropriate pharmacovigilance for adverse reactions is indicated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adverse drug reaction reports for cardiometabolic drugs from sub-Saharan Africa: a study in VigiBase.Trop Med Int Health. 2015 Jun;20(6):797-806. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12481. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Trop Med Int Health. 2015. PMID: 25704305
-
Serious adverse events reported with benzimidazole derivatives: A disproportionality analysis from the World Health Organization's pharmacovigilance database.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Nov 6;18(11):e0012634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012634. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39504320 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Review of Serious Adverse Drug Reaction Reports in the Nigerian VigiFlow Database from September 2004 to December 2016.Pharmaceut Med. 2019 Apr;33(2):145-157. doi: 10.1007/s40290-019-00267-2. Pharmaceut Med. 2019. PMID: 31933250
-
Atrial fibrillation in patients treated with intravenous zoledronic or pamidronic acid: a pharmacoepidemiological study.Eur J Endocrinol. 2021 Mar;184(3):437-444. doi: 10.1530/EJE-20-0650. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33449911
-
Cardiovascular safety of rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma B-type and/or mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitors: A mixed approach combining a meta-analysis and a pharmacovigilance disproportionality analysis.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Jun-Jul;113(6-7):420-432. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2020.03.014. Epub 2020 May 1. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32418884
Cited by
-
Onchocerca volvulus microfilariae in the anterior chambers of the eye and ocular adverse events after a single dose of 8 mg moxidectin or 150 µg/kg ivermectin: results of a randomized double-blind Phase 3 trial in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana and Liberia.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Mar 15;17(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06087-3. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38491528 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Deciphering the anti-filarial potential of bioactive compounds from Ocimum sanctum: a combined experimental and computational study.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):2237-2252. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2132030. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 36415158 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of ivermectin for treatment of COVID-19: evidence beyond the hype.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 23;22(1):639. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07589-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35870876 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin-Induced Acute Psychosis in Patients Infected With COVID-19 Pneumonia.Cureus. 2022 Jun 21;14(6):e26141. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26141. eCollection 2022 Jun. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35747110 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychiatric manifestation of the drugs used in the treatment of SARS-2-CoV-2019 (COVID-19) infection and their management: An overview and practice implications.Asian J Psychiatr. 2022 Jul;73:103101. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2022.103101. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Asian J Psychiatr. 2022. PMID: 35461033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ANSM. STROMECTOL 3 mg, comprimé—Résumé des caractéristiques du produit. [cited 10 Nov 2020]. Available: http://base-donnees-publique.medicaments.gouv.fr/affichageDoc.php?specid...
-
- FDA. Ivermectin prescribing information. Available: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/050742s022lbl.pdf
-
- Duke B. Human onchocerciasis—an overview of the disease. Acta Leiden. 1990;59: 9–24. - PubMed
-
- Ackerman SJ, Kephart GM, Francis H, Awadzi K, Gleich GJ, Ottesen EA. Eosinophil degranulation: An immunologic determinant in the pathogenesis of the Mazzotti reaction in human onchocerciasis. J Immunol. 1990;144: 3961–3969. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

