Dual blockade of EGFR and CDK4/6 delays head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by inducing metabolic rewiring
- PMID: 33878394
- PMCID: PMC8153085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.004
Dual blockade of EGFR and CDK4/6 delays head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by inducing metabolic rewiring
Abstract
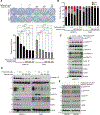
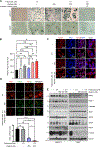
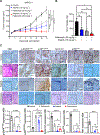
Despite preclinical success, monotherapies targeting EGFR or cyclin D1-CDK4/6 in Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) have shown a limited clinical outcome. Here, we aimed to determine the combined effect of palbociclib (CDK4/6) and afatinib (panEGFR) inhibitors as an effective strategy to target HNSCC. Using TCGA-HNSCC co-expression analysis, we found that patients with high EGFR and cyclin D1 expression showed enrichment of gene clusters associated with cell-growth, glycolysis, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition processes. Phosphorylated S6 (p-S6), a downstream effector of EGFR and cyclin D1-CDK4/6 signalling, showed a progressive increase from normal oral tissues to leukoplakia and frank malignancy, and associated with poor outcome of the patients. This increased p-S6 expression was drastically reduced after combination treatment with afatinib and palbociclib in the cell lines and mouse models, suggesting its utiliy as a prognostic marker in HNSCC. Combination treatment also reduced the cell growth and induced cell senescence via increasing reactive oxygen species with concurrent ablation of glycolytic and tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates. Finally, our findings in sub-cutaneous and genetically engineered mouse model (K14-CreERtam;LSL-KrasG12D/+;Trp53R172H/+) studies showed a significant reduction in the tumor growth and delayed tumor progression after combination treatment. This study collectively demonstrates that dual targeting may be a critical therapeutic strategy in blocking tumor progression via inducing metabolic alteration and warrants clinical evaluation.
Keywords: Cyclin D1-CDK4/6; EGFR; HNSCC; Mouse model; Senescence.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests
SKB is one of the co-founders of Sanguine Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Inc. AKG has received consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, G1 Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Genentech, Flagship Biosciences, Mirati Therapeutics and research support form Takeda. AKG also serve on a DSMC for YMAbs. Other authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Letter to the editor regarding "Dual blockade of EGFR and CDK4/6 delays head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by inducing metabolic rewiring.".Cancer Lett. 2022 Feb 28;527:191-192. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.013. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35115094 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Cancer Lett. 2022 Feb 28;527:193-194. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.020. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35115095 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Macha MA, Rachagani S, Chaudhary S, Sayed Z, Jones DT, Batra SK, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling Pathways as a Goldmine for Targeted Therapy in Head and Neck Cancers, Gene Regulation and Therapeutics for Cancer, 163.
-
- Chaudhary S, Dam V, Ganguly K, Sharma S, Atri P, Chirravuri-Venkata R, Cox JL, Sayed Z, Jones DT, Ganti AK, Ghersi D, Macha MA, Batra SK, Differential mutation spectrum and immune landscape in African Americans versus Whites: A possible determinant to health disparity in head and neck cancer, Cancer Letters, 492 (2020) 44–53. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

