Late gestation fetal hyperglucagonaemia impairs placental function and results in diminished fetal protein accretion and decreased fetal growth
- PMID: 33878802
- PMCID: PMC8249343
- DOI: 10.1113/JP281288
Late gestation fetal hyperglucagonaemia impairs placental function and results in diminished fetal protein accretion and decreased fetal growth
Abstract
Key points: Fetal glucagon concentrations are elevated in the setting of placental insufficiency, hypoxia and elevated stress hormones. Chronically elevated glucagon concentrations in the adult result in profound decreases in amino acid concentrations and lean body mass. Experimental elevation of fetal glucagon concentrations in a late-gestation pregnant sheep results in lower fetal amino acid concentrations, lower protein accretion and lower fetal weight, in addition to decreased placental function. This study demonstrates a negative effect of glucagon on fetal protein accretion and growth, and also provides the first example of a fetal hormone that negatively regulates placental nutrient transport and blood flow.
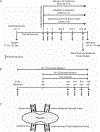
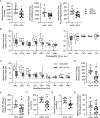
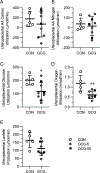
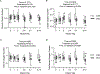
Abstract: Fetal glucagon concentrations are elevated in the setting of placental insufficiency and fetal stress. Postnatal studies have demonstrated the importance of glucagon in amino acid metabolism, and limited fetal studies have suggested that glucagon inhibits umbilical uptake of certain amino acids. We hypothesized that chronic fetal hyperglucagonaemia would decrease amino acid transfer and increase amino acid oxidation by the fetus. Late gestation singleton fetal sheep received a direct intravenous infusion of glucagon (GCG; 5 or 50 ng/kg/min; n = 7 and 5, respectively) or a vehicle control (n = 10) for 8-10 days. Fetal and maternal nutrient concentrations, uterine and umbilical blood flows, fetal leucine flux, nutrient uptake rates, placental secretion of chorionic somatomammotropin (CSH), and targeted placental gene expression were measured. GCG fetuses had 13% lower fetal weight compared to controls (P = 0.0239) and >28% lower concentrations of 16 out of 21 amino acids (P < 0.02). Additionally, protein synthesis was 49% lower (P = 0.0005), and protein accretion was 92% lower in GCG fetuses (P = 0.0006). Uterine blood flow was 33% lower in ewes with GCG fetuses (P = 0.0154), while umbilical blood flow was similar. Fetal hyperglucagonaemia lowered uterine uptake of 10 amino acids by >48% (P < 0.05) and umbilical uptake of seven amino acids by >29% (P < 0.04). Placental secretion of CSH into maternal circulation was reduced by 80% compared to controls (P = 0.0080). This study demonstrates a negative effect of glucagon on fetal protein accretion and growth. It also demonstrates that glucagon, a hormone of fetal origin, negatively regulates maternal placental nutrient transport function, placental CSH production and uterine blood flow.
Keywords: amino acid; chorionic somatomammotropin; fetal growth; fetal leucine metabolism; fick principle; glucagon; placenta; transplacental diffusion.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2021 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







Comment in
-
Back-seat driver: the fetus is not a passive passenger!J Physiol. 2021 Jul;599(13):3257-3258. doi: 10.1113/JP281791. Epub 2021 Jun 15. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33963558 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahren B (2015). Glucagon--Early breakthroughs and recent discoveries. Peptides 67, 74–81. - PubMed
-
- Alexander EK, Robinson M, Staniec M & Dluhy RG. (2002). Peripheral amino acid and fatty acid infusion for the treatment of necrolytic migratory erythema in the glucagonoma syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 57, 827–831. - PubMed
-
- Angiolini E, Coan PM, Sandovici I, Iwajomo OH, Peck G, Burton GJ, Sibley CP, Reik W, Fowden AL & Constância M. (2011). Developmental adaptations to increased fetal nutrient demand in mouse genetic models of Igf2-mediated overgrowth. The FASEB Journal 25, 1737–1745. - PubMed
-
- Ayuso-Parrilla MS, Martin-Requero A, Perez-Dias J & Parrilla R. (1976). Role of glucagon on the control of hepatic protein synthesis and degradation in the rat in vivo. The Journal of biological chemistry 251, 7785–7790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NIH R01-753 HD079404/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Award
- R01 DK088139/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD079404/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NIH R01-HD093701/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Award
- R01 HD093701/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NIH S10-OD023553/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Award
- NIH T32HD007186/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Award
- S10 OD023553/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- NIH R01-DK108910/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Award
- T32 HD007186/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NIH R01-DK088139/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Award
- R01DK108910/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 DK108910/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

