Gene fusion of IL7 involved in the regulation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 33878985
- PMCID: PMC8064517
- DOI: 10.1177/1753466621995045
Gene fusion of IL7 involved in the regulation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a rare form of immune-mediated interstitial lung disease characterized by progressive pulmonary fibrosis and scarring. The pathogenesis of IPF is still unclear. Gene fusion events exist universally during transcription and show alternated patterns in a variety of lung diseases. Therefore, the comprehension of the function of gene fusion in IPF might shed light on IPF pathogenesis research and facilitate treatment development.
Methods: In this study, we included 91 transcriptome datasets from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), including 52 IPF patients and 39 healthy controls. We detected fusion events in these datasets and probed gene fusion-associated differential gene expression and functional pathways. To obtain robust results, we corrected the batch bias across different projects.
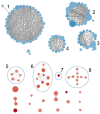
Results: We identified 1550 gene fusion events in all transcriptomes and studied the possible impacts of IL7 = AC083837.1 gene fusion. The two genes locate adjacently in chromosome 8 and share the same promoters. Their fusion is associated with differential expression of 282 genes enriched in six Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways and 35 functional gene sets. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis shows that IL7 = AC083837.1 gene fusion is associated with the enrichment of 187 gene sets. The co-expression network of interleukin-7 (IL7) indicates that decreased IL7 expression is associated with many pathways that regulate IPF progress.
Conclusion: Based on the results, we conclude that IL7 = AC083837.1 gene fusion might exacerbate fibrosis in IPF via enhancing activities of natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, skin cell apoptosis, and vessel angiogenesis, the interaction of which contributes to the development of fibrosis and the deterioration of respiratory function of IPF patients. Our work unveils the possible roles of gene fusion in regulating IPF and demonstrates that gene fusion investigation is a valid approach in probing immunologic mechanisms and searching potential therapeutic targets for treating IPF.The reviews of this paper are available via the supplemental material section.
Keywords: IL7; IPF; angiogenesis; apoptosis; fibrosis; fusion gene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Bullers K. Merck manuals. J Med Libr Assoc 2016; 104: 369–371.
-
- Xaubet A, Ancochea J, Molina-Molina M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Med Clin (Barc) 2017; 148: 170–175. - PubMed
-
- Agostini C, Semenzato G. Immunology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 1996; 2: 364–369. - PubMed
-
- Heukels P, Moor CC, von der Thusen JH, et al. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir Med 2019; 147: 79–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

