Standardized artificially created stable pertrochanteric femur fractures present more homogenous results compared to osteotomies for orthopaedic implant testing
- PMID: 33879133
- PMCID: PMC8058974
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-021-04234-4
Standardized artificially created stable pertrochanteric femur fractures present more homogenous results compared to osteotomies for orthopaedic implant testing
Abstract
Background: With regard to biomechanical testing of orthopaedic implants, there is no consensus on whether artificial creation of standardized bone fractures or their simulation by means of osteotomies result in more realistic outcomes. Therefore, the aim of this study was to artificially create and analyze in an appropriate setting the biomechanical behavior of standardized stable pertrochanteric fractures versus their simulation via osteotomizing.
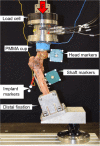
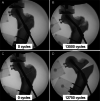
Methods: Eight pairs of fresh-frozen human cadaveric femora aged 72.7 ± 14.9 years (range 48-89 years) were assigned in paired fashion to two study groups. In Group 1, stable pertrochanteric fractures AO/OTA 31-A1 were artificially created via constant force application on the anterior cortex of the femur through a blunt guillotine blade. The same fracture type was simulated in Group 2 by means of osteotomies. All femora were implanted with a dynamic hip screw and biomechanically tested in 20° adduction under progressively increasing physiologic cyclic axial loading at 2 Hz, starting at 500 N and increasing at a rate of 0.1 N/cycle. Femoral head fragment movements with respect to the shaft were monitored by means of optical motion tracking.
Results: Cycles/failure load at 15° varus deformation, 10 mm leg shortening and 15° femoral head rotation around neck axis were 11324 ± 848/1632.4 ± 584.8 N, 11052 ± 1573/1605.2 ± 657.3 N and 11849 ± 1120/1684.9 ± 612.0 N in Group 1, and 10971 ± 2019/1597.1 ± 701.9 N, 10681 ± 1868/1568.1 ± 686.8 N and 10017 ± 4081/1501.7 ± 908.1 N in Group 2, respectively, with no significant differences between the two groups, p ≥ 0.233.
Conclusion: From a biomechanical perspective, by resulting in more consistent outcomes under dynamic loading, standardized artificial stable pertrochanteric femur fracture creation may be more suitable for orthopaedic implant testing compared to osteotomizing the bone.
Keywords: Fracture biomechanics; Fracture line analysis; Fracture model; Fracture standardization; Osteotomy; Proximal femur fracture; Stable pertrochanteric fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Panagopoulos A, Kyriakopoulos G, Anastopoulos G, Megas P, Kourkoulis SK. Design of Improved Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment (DRIFT) Study: Protocol for Biomechanical Testing and Finite Element Analysis of Stable and Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated With Intramedullary Nailing or Dynamic Compression Screw. JMIR Res Protoc. 2019;8(7):e12845. doi: 10.2196/12845. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stoffel K, Klaue K, Perren SM. Functional load of plates in fracture fixation in vivo and its correlate in bone healing. Injury. 2000;31(Suppl 2):S-B37-50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

