SNRPD1 confers diagnostic and therapeutic values on breast cancers through cell cycle regulation
- PMID: 33879154
- PMCID: PMC8059192
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01932-w
SNRPD1 confers diagnostic and therapeutic values on breast cancers through cell cycle regulation
Abstract
Background: SNRPD1 is a spliceosome-associated protein and has previously been implicated with important roles in cancer development.
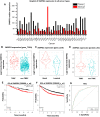
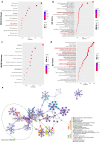
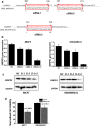
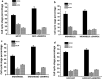
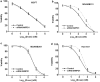
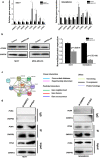
Methods: Through analyzing the differential expression patterns and clinical association of splicing associated genes among tumor and tumor adjacent samples across different tumors and among different breast cancer subtypes, we identify the tumor promotive role of SNRPD1 using multiple publicly available datasets. Through pathway, gene ontology enrichment analysis and network construction, we linked the onco-therapeutic role of SNRPD1 with cell cycle. Via a series of experimental studies including knockdown assay, qPCR, western blotting, cell cycle, drug response assay, we confirmed the higher expression of SNPRD1 at both gene and protein expression levels in triple negative breast cancer cells, as well as its roles in promoting cell cycle and chemotherapy response.
Results: Our study revealed that SNRPD1 over-expression was significantly associated with genes involved in cell cycle, cell mitosis and chromatin replication, and silencing SNRPD1 in breast cancer cells could lead to halted tumor cell growth and cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 stage. We also found that triple negative breast cancer cells with reduced SNRPD1 expression lost certain sensitivity to doxorubicin whereas luminal cancer cells did not.
Conclusions: Our results suggested the prognostic value of SNRPD1 on breast cancer survival, its potential as the therapeutic target halting cell cycle progression for breast cancer control, and warranted special attention on the combined use of doxorubicin and drugs targeting SNRPD1.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cell cycle arrest; Prognosis; SNRPD1; Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
SNRPD1 conveys prognostic value on breast cancer survival and is required for anthracycline sensitivity.BMC Cancer. 2023 Apr 25;23(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10860-z. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37098488 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Level of Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein D1 in Gastric Cancer and Its Effect on Prognosis.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2025 Feb;47(1):1-9. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.16097. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40082221
-
The Potential Role of SNRPD1 Stabilized by IGF2BP2 in the Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024 Oct 11;16:679-688. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S481549. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024. PMID: 39411513 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic significance of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Sm D1 aberrantly high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer. 2022 Jan 1;13(1):184-201. doi: 10.7150/jca.65225. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34976182 Free PMC article.
-
p53 in breast cancer subtypes and new insights into response to chemotherapy.Breast. 2013 Aug;22 Suppl 2:S27-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.07.005. Breast. 2013. PMID: 24074787 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemoproteomics reveals proteome-wide covalent and non-covalent targets of withaferin A.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jun;46(6):1782-1793. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01468-5. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39900821
-
Atmospheric pressure plasma treatment increases the antioxidant capacity of the serum in vitro.Sci Rep. 2025 May 31;15(1):19127. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03914-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40450058 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpressed SNRPB/D1/D3/E/F/G correlate with poor survival and immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jun 15;14(6):4207-4228. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35836882 Free PMC article.
-
DAB2IP loss in luminal a breast cancer leads to NF-κB-associated aggressive oncogenic phenotypes.JCI Insight. 2024 Dec 6;9(23):e171705. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.171705. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39418101 Free PMC article.
-
Carcinogenesis and Prognostic Utility of Arginine Methylation-Related Genes in Hepatocellular Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 24;45(12):9422-9430. doi: 10.3390/cimb45120591. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38132437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonnal S, Vigevani L, Valcarcel J. The spliceosome as a target of novel antitumour drugs. Nat Rev. 2012;11:847–857. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

