Split-VMAT technique to control the deep inspiration breath hold time for breast cancer radiotherapy
- PMID: 33879209
- PMCID: PMC8056647
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-021-01800-x
Split-VMAT technique to control the deep inspiration breath hold time for breast cancer radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: To improve split-VMAT technique by optimizing treatment delivery time for deep-inspiration breath hold (DIBH) radiotherapy in left-sided breast cancer patients, when automatic beam-interruption devices are not available.
Methods: Ten consecutive patients were treated with an eight partial arcs (8paVMAT) plan, standard of care in our center. A four partial arcs (4paVMAT) plan was also created and actual LINAC outputs were measured, to evaluate whether there was a dosimetric difference between both techniques and potential impact on the delivered dose. Subsequently, ten other patients were consecutively treated with a 4paVMAT plan to compare the actual treatment delivery time between both techniques. The prescribed dose was 40.05 Gy/15 fractions on the PTV breast (breast or thoracic wall), lymph nodes (LN) and intramammary lymph node chain (IMN). Treatment delivery time, PTVs coverage, conformity index (CI), organs at risk (OAR) dose, monitor units (MU), and gamma index were compared.
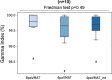
Results: Both split-VMAT techniques resulted in similar dose coverage for the PTV Breast and LN, and similar CI. For PTV IMN we observed a 5% increased coverage for the volume receiving ≥ 36 Gy with 4paVMAT, with an identical volume receiving ≥ 32 Gy. There was no difference for the OAR sparing, with the exception of the contralateral organs: there was a 0.6 Gy decrease for contralateral breast mean (p ≤ 0.01) and 1% decrease for the volume of right lung receiving ≥ 5 Gy (p = 0.024). Overall, these results indicate a modest clinical benefit of using 4paVMAT in comparison to 8paVMAT. An increase in the number of MU per arc was observed for the 4paVMAT technique, as expected, while the total number of MU remained comparable for both techniques. All the plans were measured with the Delta4 phantom and passed the gamma index criteria with no significant differences. Finally, the main difference was seen for the treatment delivery time: there was a significant decrease from 8.9 to 5.4 min for the 4paVMAT plans (p < .05).
Conclusions: This study is mainly of interest for centers who are implementing the DIBH technique without automatic beam-holding devices and who therefore may require to manually switch the beam on and off during breast DIBH treatment. Split-VMAT technique with 4 partial arcs significantly reduces the treatment delivery time compared to 8 partial arcs, without compromising the target coverage and the OAR sparing. The technique decreases the number of breath holds per fraction, resulting in a shorter treatment session.
Keywords: Deep inspiration breath-hold; SGRT; Split-VMAT.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Poeta has nothing to disclose. Dr. Jourani has nothing to disclose. Dr. De Caluwé reports grants from AstraZeneca, outside the submitted work. Dr. Van den Begin has nothing to disclose. Dr. Van Gestel reports being a member of the Advisory board or receiving honoraria from Sanofi, Accuray, Takeda, Merck-Pfizer and Novartis. Dr. Reynaert has nothing to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dosimetric advantages of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) with deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH) technique in Halcyon Linac for left breast cancer treatment.Med Dosim. 2022 Autumn;47(3):288-294. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2022.04.005. Epub 2022 May 28. Med Dosim. 2022. PMID: 35641365
-
Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) vs. volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) in deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) technique in left-sided breast cancer patients-comparative analysis of dose distribution and estimation of projected secondary cancer risk.Strahlenther Onkol. 2023 Jan;199(1):90-101. doi: 10.1007/s00066-022-01979-2. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Strahlenther Onkol. 2023. PMID: 35943553
-
Minimizing normal tissue low dose bath for left breast Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) using jaw offset.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Aug;25(8):e14365. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14365. Epub 2024 May 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38760907 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Deep Inspiration Breath Hold and Free Breathing in Proton Beam Therapy Plans for Breast Cancer Radiotherapy.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2025 Apr;40:103782. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2025.103782. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2025. PMID: 39999640
-
Clinical benefits of deep inspiration breath-hold in postoperative radiotherapy for right-sided breast cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 8;24(1):1238. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12992-2. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39379827 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Hybrid VMAT Advantages and Robustness Considering Setup Errors Using Surface Guided Dose Accumulation for Internal Lymph Mammary Nodes Irradiation of Postmastectomy Radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 22;12:907181. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.907181. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35936730 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Inspiratory Breath-Hold Technique for Patients with Left-Sided Breast Cancer: Dosimetric Analysis, Clinical Evaluation, and Prediction.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15330338251329120. doi: 10.1177/15330338251329120. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40211790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simonetto C, Eidemüller M, Gaasch A, Pazos M, Schönecker S, Reitz D, Kääb S, Braun M, Harbeck N, Niyazi M, Belka C, Corradini S. Does deep inspiration breath-hold prolong life? Individual risk estimates of ischaemic heart disease after breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2019;131:202–207. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.07.024. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

