β-arrestin-dependent PI(4,5)P2 synthesis boosts GPCR endocytosis
- PMID: 33879605
- PMCID: PMC8092559
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2011023118
β-arrestin-dependent PI(4,5)P2 synthesis boosts GPCR endocytosis
Abstract
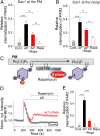
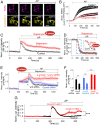
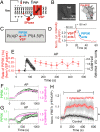
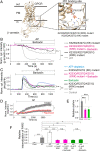
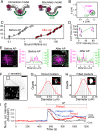
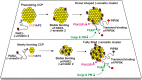
β-arrestins regulate many cellular functions including intracellular signaling and desensitization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Previous studies show that β-arrestin signaling and receptor endocytosis are modulated by the plasma membrane phosphoinositide lipid phosphatidylinositol-(4, 5)-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2). We found that β-arrestin also helped promote synthesis of PI(4,5)P2 and up-regulated GPCR endocytosis. We studied these questions with the Gq-coupled protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2), which activates phospholipase C, desensitizes quickly, and undergoes extensive endocytosis. Phosphoinositides were monitored and controlled in live cells using lipid-specific fluorescent probes and genetic tools. Applying PAR2 agonist initiated depletion of PI(4,5)P2, which then recovered during rapid receptor desensitization, giving way to endocytosis. This endocytosis could be reduced by various manipulations that depleted phosphoinositides again right after phosphoinositide recovery: PI(4)P, a precusor of PI(4,5)P2, could be depleted at either the Golgi or the plasma membrane (PM) using a recruitable lipid 4-phosphatase enzyme and PI(4,5)P2 could be depleted at the PM using a recruitable 5-phosphatase. Endocytosis required the phosphoinositides. Knock-down of β-arrestin revealed that endogenous β-arrestin normally doubles the rate of PIP5-kinase (PIP5K) after PAR2 desensitization, boosting PI(4,5)P2-dependent formation of clathrin-coated pits (CCPs) at the PM. Desensitized PAR2 receptors were swiftly immobilized when they encountered CCPs, showing a dwell time of ∼90 s, 100 times longer than for unactivated receptors. PAR2/β-arrestin complexes eventually accumulated around the edges or across the surface of CCPs promoting transient binding of PIP5K-Iγ. Taken together, β-arrestins can coordinate potentiation of PIP5K activity at CCPs to induce local PI(4,5)P2 generation that promotes recruitment of PI(4,5)P2-dependent endocytic machinery.
Keywords: GPCR; PIP5K; endocytosis; phosphoinositide lipids; β.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contributions of protein kinases and β-arrestin to termination of protease-activated receptor 2 signaling.J Gen Physiol. 2016 Mar;147(3):255-71. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201511477. J Gen Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26927499 Free PMC article.
-
β-arrestins and G protein-coupled receptor trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;219:173-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41199-1_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24292830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis pathways using real-time monitoring of agonist-promoted interaction between beta-arrestins and AP-2.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29089-100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700577200. Epub 2007 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17675294
-
Membrane phosphoinositides regulate GPCR-β-arrestin complex assembly and dynamics.Cell. 2022 Nov 23;185(24):4560-4573.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.018. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Cell. 2022. PMID: 36368322 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-Dependent and -Independent Internalization of G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Methods, Mechanisms, and Implications on Cell Signaling.Mol Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;99(4):242-255. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.120.000192. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33472843 Review.
Cited by
-
Determining the Effects of Differential Expression of GRKs and β-arrestins on CLR-RAMP Agonist Bias.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 29;13:840763. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.840763. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35422711 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin: an overlooked regulator of endocytosis and endosomal sorting?Biol Open. 2022 Jan 15;11(1):bio059057. doi: 10.1242/bio.059057. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Biol Open. 2022. PMID: 35076063 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules targeting endocytic uptake and recycling pathways.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 10;11:1125801. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1125801. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36968200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biophysical physiology of phosphoinositide rapid dynamics and regulation in living cells.J Gen Physiol. 2022 Jun 6;154(6):e202113074. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202113074. Epub 2022 May 18. J Gen Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35583815 Free PMC article.
-
Discrete GPCR-triggered endocytic modes enable β-arrestins to flexibly regulate cell signaling.Elife. 2022 Oct 17;11:e81563. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81563. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36250629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Posor Y., Eichhorn-Grünig M., Haucke V., Phosphoinositides in endocytosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1851, 794–804 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Luttrell L. M., Lefkowitz R. J., The role of beta-arrestins in the termination and transduction of G-protein-coupled receptor signals. J. Cell Sci. 115, 455–465 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

