Acupoint catgut embedding for the treatment of peptic ulcers: A protocol for systematic review and meta analysis
- PMID: 33879710
- PMCID: PMC8078472
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025562
Acupoint catgut embedding for the treatment of peptic ulcers: A protocol for systematic review and meta analysis
Abstract
Background: Peptic ulcer (PU) is a common clinical disease of the digestive system, which can occur in all ages, gastric and duodenal ulcers are the most commonly seen PUs in clinical practice. The main manifestations are chronic and periodic rhythmic upper abdominal pain, accompanied by indigestion symptoms such as pantothenic acid, belching, and nausea. Serious complications such as bleeding, perforation, obstruction and canceration are easy to occur, endangering the life safety of patients. There are many ways to treat PU in clinic, and acupoint catgut embedding therapy has its unique advantages. Hence, our systematic review aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of acupoint embedding therapy in the treatment of PU and to provide a reliable basis for physician.
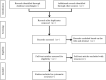
Methods: We will search electronic databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Database (WF), China Biomedical Literature Database (CBM), and China Scientific Journals Database (VIP) from establishment to April 2021, and will manually searched the list of medical journals as a supplement. Two authors will screen the studies independently, as well as extract data information, and assess methodological quality through the Cochrane risk of bias (ROB) tool. The Stata software (Version 16.0) software will be used for statistical analysis.
Results: By evaluating the current status of acupoint catgut embedding for Peptic ulcer disease, this study would prove the effectiveness and safety of acupoint embedding therapy, and will be published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Conclusion: This systematic review will provide a credible evidence-based for acupoint catgut embedding in the treatment of peptic ulcer.
Inplasy registration number: INPLASY202130097.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang WD, Li JX, Chen ZS, et al. Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcer with integrated traditional Chinese and Western Medicine (Tianjin, 2011). Chin J Integr Med 2012;32:733–7. - PubMed
-
- Yao P. Clinical observation on the 44 cases of acupoint catgut embedding therapy for peptic ulcer. Tian J Trad Chin Med 2015;32:728–31.
-
- Wei HR. Acupoint catgut embedding combined with Huangqi Jianzhong Decoction in the treatment of 40 cases of peptic ulcer. Inner Mongolia J Trad Chin Med 2013;32:29–30.
-
- Ren SF. Analysis of relative factors associated with peptic ulcer. Shanxi Med Sci 2012.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous