ARIH1 signaling promotes anti-tumor immunity by targeting PD-L1 for proteasomal degradation
- PMID: 33879767
- PMCID: PMC8058344
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22467-8
ARIH1 signaling promotes anti-tumor immunity by targeting PD-L1 for proteasomal degradation
Abstract
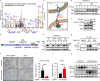
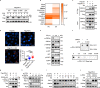
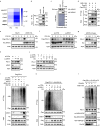
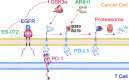
Cancer expression of PD-L1 suppresses anti-tumor immunity. PD-L1 has emerged as a remarkable therapeutic target. However, the regulation of PD-L1 degradation is not understood. Here, we identify several compounds as inducers of PD-L1 degradation using a high-throughput drug screen. We find EGFR inhibitors promote PD-L1 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation following GSK3α-mediated phosphorylation of Ser279/Ser283. We identify ARIH1 as the E3 ubiquitin ligase responsible for targeting PD-L1 to degradation. Overexpression of ARIH1 suppresses tumor growth and promotes cytotoxic T cell activation in wild-type, but not in immunocompromised mice, highlighting the role of ARIH1 in anti-tumor immunity. Moreover, combining EGFR inhibitor ES-072 with anti-CTLA4 immunotherapy results in an additive effect on both tumor growth and cytotoxic T cell activation. Our results delineate a mechanism of PD-L1 degradation and cancer escape from immunity via EGFR-GSK3α-ARIH1 signaling and suggest GSK3α and ARIH1 might be potential drug targets to boost anti-tumor immunity and enhance immunotherapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biochemical analysis of PD-L1 ubiquitination by CRL3SPOP, ARIH1, and NEDD4 family ubiquitin ligases.Structure. 2025 Aug 7;33(8):1304-1313.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2025.05.005. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Structure. 2025. PMID: 40472843 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-Associated RING-CH 8 Functions as a Novel PD-L1 E3 Ligase to Mediate PD-L1 Degradation Induced by EGFR Inhibitors.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Oct;19(10):1622-1634. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0147. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34183449 Free PMC article.
-
ARIH1 activates STING-mediated T-cell activation and sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint blockade.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 10;14(1):4066. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39920-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37429863 Free PMC article.
-
New horizons in the mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for PD-L1 protein degradation in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Sep;1879(5):189152. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189152. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38992509 Review.
-
Posttranslational Modifications of PD-L1 and Their Applications in Cancer Therapy.Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 15;78(22):6349-6353. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1892. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30442814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor immune checkpoints and their associated inhibitors.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Oct 15;23(10):823-843. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200195. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 36226537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin modification in the regulation of tumor immunotherapy resistance mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Aug 30;13(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00552-0. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39223632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LSD1 deletion decreases exosomal PD-L1 and restores T-cell response in gastric cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 16;21(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01557-1. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35296335 Free PMC article.
-
Neural regulations of the tumor microenvironment.FASEB Bioadv. 2021 Sep 12;4(1):29-42. doi: 10.1096/fba.2021-00066. eCollection 2022 Jan. FASEB Bioadv. 2021. PMID: 35024571 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational regulatory mechanism of PD-L1 in cancers and associated opportunities for novel small-molecule therapeutics.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 May 31;56(10):1415-1424. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024085. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38826132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

