[Semiquantitative parameters of 18F-FDG PET/CT, gene mutation states of epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase in prognosis evaluation of patients with lung adenocarcinoma]
- PMID: 33879893
- PMCID: PMC8072443
- DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.003
[Semiquantitative parameters of 18F-FDG PET/CT, gene mutation states of epidermal growth factor receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase in prognosis evaluation of patients with lung adenocarcinoma]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the valuable predictors for evaluating progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with lung adenocarcinoma, we analyzed the potential roles of standardized uptake value (SUV)-derived parameters from 18F-FDG PET/CT, combining with the gene mutation states of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), and other clinical characteristics.
Methods: Data of 84 lung adenocarcinoma patients pre-treated, who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT scans, EGFR gene mutations test, ALK rearrangement assay and other relative tests, were retrospectively collected. Then a series of clinical parameters including EGFR/ALK mutation status and SUV-derived features [maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), average of standardized uptake value (SUVmean), metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and total lesion glycolysis (TLG)] were evaluated. Best possible cutoff points for all measuring parameters were calculated using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis. Survival analysis was performed using Cox proportional hazards model to determine the prognostic markers for progression-free survival (PFS). Survival curves were obtained through Log-rank test and Kaplan-Meier curve.
Results: The median follow-up period was 31 months (24 to 58 months). It was found that SUVmax (≥3.01), SUVmean (≥2.25), MTV (≥25.41 cm3), and TLG (≥55.02) of the primary tumors were significantly associated with PFS in univariate Cox proportional hazards regression. Then regardless of age, gender, co-morbidity, EGFR/ALK mutation status, and treatment program, TLG (≥ 55.02, HR=4.965, 95%CI: 1.360-18.133), TNM stage (Ⅲ/Ⅳ, HR=7.811, 95%CI: 2.977-20.489), pro-gastrin releasing peptide (proGRP) (≥45.65 ng/L, HR=4.070, 95%CI: 1.442-11.487), tissue polypeptide antigen (TPA) (≥68.20 U/L, HR=6.996, 95%CI: 1.458-33.574), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (≥82.50 IU/L, HR=4.160, 95%CI: 1.416-12.219) and ratio of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTTR) (≥1.16: HR=4.58, 95%CI: 1.913-10.946) showed the independently relevant to PFS through multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis. The EGFR mutant (P=0.343) and ALK rearrangement (P=0.608) were not significant either in survival analysis.
Conclusion: High SUV-derived parameters (SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV and TLG) might provide prognostic value to some extent. Especially, TLG, and other clinical features [TNM stage, proGRP, TPA, ALP, and aPTTR] could be independently and significantly associated with PFS of lung adenocarcinoma patients. However, EGFR/ALK gene status could not be effectively relevant to PFS in lung adenocarcinoma patients.
目的: 评估18F-FDG PET/CT半定量参数、表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)和间变淋巴瘤激酶(anaplastic lymphoma kinase,ALK)基因突变状态对肺腺癌患者预后评估的价值。
方法: 回顾性收集84名肺腺癌患者术前18F-FDG PET/CT半定量参数,EGFR及ALK基因突变检查结果。18F-FDG PET/CT半定量参数分别为:最大标准化摄取值(maximum standardized uptake value,SUVmax)、平均标准化摄取值(average of standardized uptake value,SUVmean)、肿瘤代谢体积(metabolic tumor volume,MTV)和总糖酵解量(total lesion glycolysis,TLG)。连续变量用ROC曲线分析法转为分类变量,生存分析采用Cox比例风险回归分析,生存曲线经Log-rank检验和Kaplan-Meier法获得。
结果: 患者平均随访期31个月(24~58个月)。单因素分析显示,原发灶SUVmax、SUVmean、MTV及TLG与无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)显著相关。多因素Cox比例风险回归分析显示,不论年龄、性别、合并症、EGFR或ALK基因突变与否及治疗情况,TLG(≥55.02,HR=4.965,95%CI:1.360~18.133)、TNM分期(Ⅲ/Ⅳ期,HR=7.811,95%CI:2.977~20.489)、胃泌素释放肽前体(pro-gastrin releasing peptide,proGRP)(≥45.65 ng/L,HR=4.070,95%CI:1.442~11.487)、组织多肽抗原(tissue polypeptide antigen,TPA)(≥68.20 U/L,HR=6.996,95%CI:1.458~33.574)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)(≥82.50 IU/L,HR=4.160,95%CI:1.416~12.219)和活化部分凝血活酶时间比值(ratio of activated partial thromboplastin time,aPTTR)(≥1.16,HR=4.576,95%CI:1.913~10.946)为独立显著预后因素。EGFR(P=0.343)或ALK(P=0.608)基因突变状态均与PFS无显著相关。
结论: 原发灶高水平18F-FDG PET/CT半定量参数(SUVmax、SUVmean、MTV和TLG)对肺腺癌患者具有不同程度的预后评估价值,TNM分期、proGRP、TPA、ALP和aPTTR均与PFS存在独立、显著关联,EGFR或ALK基因突变状态与PFS未见明确相关。
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Anaplastic lymphoma kinase; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Lung neoplasms; Positron-emission tomography.
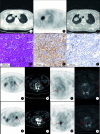
Figures



References
-
-
Noone A, Howlader N, Krapcho M, et al. SEER cancer statistics review (CRS), 1975-2015 [EB/OL]. (2018-09-10) [2018-09-10]. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/.
-
-
- Salavati A, Duan F, Snyder BS, et al. Optimal FDG PET/CT volumetricparameters for risk stratification in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: results from the ACRIN 6668/RTOG 0235 trial. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(12):1969–1983. doi: 10.1007/s00259-017-3753-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
