Assessment of prescription pattern at primary healthcare centres in Khartoum locality, Sudan
- PMID: 33879939
- PMCID: PMC8026004
- DOI: 10.24911/SJP.106-1585060471
Assessment of prescription pattern at primary healthcare centres in Khartoum locality, Sudan
Abstract
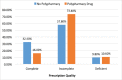
To promote rational drug use in developing countries, it is important to assess drug use pattern, using the World Health Organisation (WHO) drug indicators. The aim of this study was to assess the prescription patterns at the primary healthcare centres in Khartoum locality, compare prescription habits between consultants and medical officers and identify polypharmacy and its effect on prescription quality using WHO drug indicators. The study was descriptive and cross-sectional. The sample was selected using systematic random sampling. Five hundred and four patient prescriptions were reviewed. The study showed that the average number of drugs prescribed per encounter was 2.4%, the percentage of drugs' generic name was 49.8% the percentage of encounter with antibiotic was 34.1%. Other important components for completeness of prescription including prescribers name were mentioned in almost all encounters, whereas the patient's age was stated in 38.3%. Drug strength, quality and doses frequency were stated in 64.1%, 69.4% and 70.4%, respectively. Consultant tendency towards polypharmacy prescription was in 14.9% compared to medical officers (85.1%). The quality of prescriptions was classified as complete, incomplete or deficient with 29.4%, 60.7% and 9.9%, respectively.
Keywords: Khartoum; Prescription pattern; Primary health centres; Sudan.
Copyright © Sudanese Association of Pediatricians.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. The pursuit of responsible use of medicines: sharing and learning from country experiences. WHO/EMP/MAR/2012.3. Available from: www.who.int .
-
- World Health Organization. Policy perspectives on medicines-promoting rational use of medicines: core components. [2020 Aug 10];2002 Sep; Available from: www.who.int .
-
- WHO Drug Information. 2018;32(2):194–220. Available from: https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/issues/DrugIn...
-
- Desalegn AA. Assessment of drug use pattern using WHO prescribing indicators at Hawassa University teaching and referral hospital, South Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(1):170. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-13-170. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atif M, Sarwar MR, Azeem M, Umer D, Rauf A, Rasool A, et al. Assessment of WHO/INRUD core drug use indicators in two tertiary care hospitals of Bahawalpur, Punjab, Pakistan. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2016;9(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40545-016-0076-4. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources