Reliability and Validity of the Adapted Chinese Version of the Satisfaction of Adolescents with Postoperative Pain Management - Idiopathic Scoliosis (SAP-S) Scale
- PMID: 33880060
- PMCID: PMC8052124
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S301205
Reliability and Validity of the Adapted Chinese Version of the Satisfaction of Adolescents with Postoperative Pain Management - Idiopathic Scoliosis (SAP-S) Scale
Abstract
Study design: A prospective study.
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the internal reliability and structure validity of an adapted simplified Chinese version of the Satisfaction of Adolescents with Postoperative pain management - idiopathic Scoliosis (SAP-S) scale in mainland China.
Summary of background data: Pain management is a major issue for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) patients undergoing posterior spinal fusions. There is a lack of valid scales for evaluating patients' satisfaction with postoperative pain management. The SAP-S was proven to be a valid and reliable measure in English and French.
Methods: The SAP-S was translated into Chinese according to the internationally recognized guidelines. A total of 95 AIS patients undergoing posterior fusion surgery completed the CSAP-S, along with other self-reported questionnaires, including the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) and Scoliosis Research Society-22 (SRS-22) questionnaires. The internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and construct validity of the CSAP-S were determined.
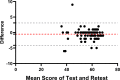
Results: The SAP-S was successfully translated into Chinese. All patients completed the CSAP-S twice and the other instruments. The CSAP-S had good internal consistency and test-retest reliability with Cronbach's alpha coefficient measuring 0.895 and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) measuring 0.97. Elimination of any one item did not result in a value of Cronbach's alpha of <0.80. A good construct validity was shown by good correlation with bodily pain (r=0.883, p=0.004) and social functioning (r=0.786, p=0.002) domains of SF-36 and pain (r=0.752, p=0.001) and satisfaction with management (r=0.746, p=0.005) domains of SRS-22.
Conclusion: The CSAP-S demonstrated good internal consistency, reliability, and construct validity, and may be used for the evaluation of AIS patients' satisfaction with postoperative pain management in mainland China.
Keywords: Chinese adaptation; SAP-S; idiopathic scoliosis; pain management; satisfaction.
© 2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and validity of the adapted Dutch version of the revised Scoliosis Research Society 22-item questionnaire.Spine J. 2014 Aug 1;14(8):1663-72. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.09.046. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24360746
-
Validity and reliability of an adapted Thai version of Scoliosis Research Society-22 questionnaire for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Apr 20;37(9):783-7. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318230a92d. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 22517481
-
Adapted simplified Chinese (mainland) version of Scoliosis Research Society-22 questionnaire.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009 May 20;34(12):1321-4. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31819812b7. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. PMID: 19455008
-
Reliability and validity of a cross-culturally adapted Hindi version of the SRS-22r questionnaire in Indian patients.Spine Deform. 2020 Oct;8(5):885-891. doi: 10.1007/s43390-020-00106-4. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Spine Deform. 2020. PMID: 32253737
-
Reliability generalization meta-analysis of the Athens Insomnia Scale and its translations: Examining internal consistency and test-retest validity.Sleep Med. 2023 Nov;111:133-145. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2023.09.015. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Sleep Med. 2023. PMID: 37776584 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous