Bioactive Compounds and Traditional Herbal Medicine: Promising Approaches for the Treatment of Dementia
- PMID: 33880073
- PMCID: PMC8051957
- DOI: 10.2147/DNND.S299589
Bioactive Compounds and Traditional Herbal Medicine: Promising Approaches for the Treatment of Dementia
Abstract
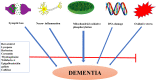
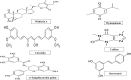
Dementia is a term that encompasses a group of clinical symptoms affecting memory, thinking and social abilities, characterized by progressive impairment of memory performance and cognitive functions. There are several factors involved in the pathogenesis and progression of dementia, such as old age, brain ischemia, toxin exposure, and oxidative stress. There are extensive similarities between dementia and Alzheimer's disease (AD) either in clinical manifestations or experimental animal models. AD is the most dominant form of dementia, characterized by the accumulation of beta-amyloid protein and cholinergic neurotransmission deficits in the brain. Currently available medications for the treatment of dementia, such as choline esterase inhibitors, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists (memantine), have short-term efficacy and only relieve symptoms rather than targeting the main underlying pathogenesis. Several animal studies and clinical trials are being conducted to provide a rational approach to these medicinal plants in the prevention or treatment of memory deficits. This review highlights the potential effects of medicinal plants and their derived lead molecules, and explains the related mechanisms and effects reviewed from published literature as major thrust aspects and hopeful strategies in the prevention or treatment of dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; bioactive compounds; cognitive impairment; dementia; medicinal plants; vascular dementia.
© 2021 Alzobaidi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources