Spinal cord compression from hypertrophic nerve roots in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy - A case report
- PMID: 33880219
- PMCID: PMC8053436
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_35_2021
Spinal cord compression from hypertrophic nerve roots in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy - A case report
Abstract
Background: Spinal cord compression secondary to nerve root hypertrophy is often attributed to hereditary neuropathies. However, to avoid misdiagnosis, rare immune-mediated neuropathy such as chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) should not be overlooked. This report presents a case of multilevel nerve root hypertrophy leading to significant cord compression from CIDP.
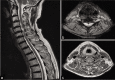
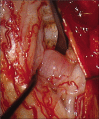
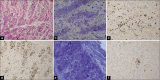
Case description: We report a 56-year-old gentleman with type two diabetes mellitus who presented with subacute cervical cord syndrome following a fall. Mixed upper and lower motor neuron features were noted on examination. Magnetic resonance imaging showed significant pan-spinal proximal nerve root hypertrophy, compressing the cervical spinal cord. Initial radiological opinion raised the possibility of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), but neurophysiology revealed both axonal and demyelinating changes that were etiologically non-specific. C6 root and sural nerve biopsies taken at cervical decompression displayed striking features suggestive for CIDP. Although NF-1 is the most observed condition associated with root hypertrophy, other important and potentially treatable differentials need to be entertained.
Conclusion: While rare, CIDP can cause significant spinal cord compression. Furthermore, clinical manifestations of CIDP can mimic those of inherited peripheral neuropathies. Neurologists and neurosurgeons should be aware of this condition to optimize subsequent therapeutic decision-making.
Keywords: Charcot-marie-tooth disease; Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy; Hypertrophic neuropathy; Neurofibromatosis.
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: two cases with cervical spinal cord compression.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2005 Sep;63(3A):666-9. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x2005000400021. Epub 2005 Sep 9. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2005. PMID: 16172720
-
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) with hypertrophic spinal radiculopathy mimicking neurofibromatosis.Acta Neuropathol. 2003 Feb;105(2):185-8. doi: 10.1007/s00401-002-0616-7. Epub 2002 Sep 28. Acta Neuropathol. 2003. PMID: 12536230
-
Magnetic resonance neurography in diagnosing childhood chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy.Brain Dev. 2021 Feb;43(2):352-356. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Brain Dev. 2021. PMID: 33433331
-
CIDP and other inflammatory neuropathies in diabetes - diagnosis and management.Nat Rev Neurol. 2017 Oct;13(10):599-611. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.123. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28914883 Review.
-
History, Diagnosis, and Management of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy.Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 Jun;93(6):777-793. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.03.026. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018. PMID: 29866282 Review.
Cited by
-
Original Surgical Treatment and Long-term Follow-up for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Causing a Compressive Cervical Myelopathy: Review of the Literature.Neurospine. 2022 Jun;19(2):472-477. doi: 10.14245/ns.2143232.616. Epub 2022 May 17. Neurospine. 2022. PMID: 35588760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin JH. Recurrent polyneuropathies and their corticosteroid treatment: With five-year observations of a placebo-controlled case treated with corticotrophin, cortisone, and prednisone. Brain. 1958;81:157–92. - PubMed
-
- Curtis-Lopez CM, Soh C, Ealing J, Evans DG, Wright EM, Vassallo G, et al. Clinical and neuroradiological characterisation of spinal lesions in adults with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;77:98–105. - PubMed
-
- Drouet A, Wolkenstein P, Lefaucheur JP, Pinson S, Combemale P, Gherardi RK, et al. Neurofibromatosis 1-associated neuropathies: A reappraisal. Brain. 2004;127:1993–2009. - PubMed
-
- Duggins AJ, Mcleod JG, Pollard JD, Davies L, Yang F, Thompson EO, et al. Spinal root and plexus hypertrophy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain. 1999;122:1383–90. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
