The Association of Acute Kidney Injury With Disease Severity and Mortality in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33880250
- PMCID: PMC8045562
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.13894
The Association of Acute Kidney Injury With Disease Severity and Mortality in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
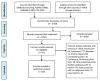
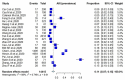
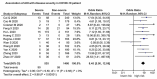
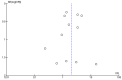
Background and objective The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has become a global healthcare emergency. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19, has a wide range of clinical manifestations ranging from subclinical infection to multi-organ failure. In addition to the respiratory system, COVID-19 also adversely affects the kidneys. In this study, we aimed to measure the prevalence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in COVID-19 and its association with the disease severity and mortality in COVID-19 patients. Materials and methods We conducted our study by following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. A comprehensive literature search using four databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Google Scholar, and clinicaltrial.gov) was performed. Our initial search returned 2,771 articles. After excluding review articles, duplicates, and non-relevant studies, we included 20 articles that reported an association between COVID-19 and AKI. We subsequently performed a random effect analysis to find the pooled prevalence, pooled odds ratio (OR) estimates, and 95% confidence intervals for severe COVID-19 and mortality outcomes in AKI using Cochrane RevMan (version 5.4) and R programming language (version 4.16-2). Results A total of 14,415 patients from various countries were included. Among the 20 cohorts, the median age was 55.8 ±8.39 years (range: 43-72 years), and 43.78% of the subjects were female. Out of a total of 14,415 patients, 3,820 developed AKI with a pooled prevalence of 11% (95% CI: 0.07-0.15; p<0.01; I2=98%). AKI was found to have a significant association with severe COVID-19 disease, with a pooled OR of 8.45 (95% CI: 5.56-12.56; p<0.00001; I2=0%). AKI was associated with significantly higher mortality in patients with COVID-19 with an OR of 13.52 (95% CI: 5.43-33.67; p<0.00001; I2=88%). Conclusion AKI manifests as a common COVID-19 complication, and COVID-19 patients with AKI generally have poor outcomes in terms of disease severity and mortality.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; acute renal failure; covid-19; sars-cov-2.
Copyright © 2021, Menon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
