Roles of miRNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Implications and Clinical Opportunities
- PMID: 33880345
- PMCID: PMC8046386
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2021.029
Roles of miRNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Implications and Clinical Opportunities
Abstract
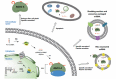
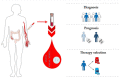
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most disseminated diseases across the globe engaging the digestive system. Various therapeutic methods from traditional to the state-of-the-art ones have been applied in CRC patients, however, the attempts have been unfortunate to lead to a definite cure. MiRNAs are a smart group of non-coding RNAs having the capabilities of regulating and controlling coding genes. By utilizing this stock-in-trade biomolecules, not only disease's symptoms can be eliminated, there may also be a good chance for the complete cure of the disease in the near future. Herein, we provide a comprehensive review delineating the therapeutic relationship between miRNAs and CRC. To this, various clinical aspects of miRNAs which act as a tumor suppressor and/or an oncogene, their underlying cellular processes and clinical outcomes, and, in particular, their effects and expression level changes in patients treated with chemo- and radiotherapy are discussed. Finally, based on the results deducted from scientific research studies, therapeutic opportunities based on targeting/utilizing miRNAs in the preclinical as well as clinical settings are highlighted.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Clinical implication; Colorectal cancer; Radiotherapy; miRNAs.
© 2021 The Authors.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources