Preparation, Statistical Optimization and Characterization of Propolis-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Using Box-Behnken Design
- PMID: 33880352
- PMCID: PMC8046400
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2021.043
Preparation, Statistical Optimization and Characterization of Propolis-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Using Box-Behnken Design
Abstract
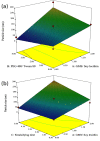
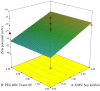
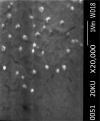
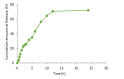
Purpose: Propolis is a resinous material obtained by honeybees with many biological and pharmacological properties which can be used for treatment of various diseases. Current study aims to formulate and characterize propolis-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) carrier system. Methods: The prepared SLNs, composed of glyceryl monostearate (GMS), Soy lecithin, Tween 80 and polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400), were fabricated employing solvent emulsification-evaporation technique. In addition, the impact of several variables including concentration ratios of GMS/Soy lecithin and PEG 400/Tween 80 along with emulsification time were evaluated on the size, polydispersity index (PDI) and zeta potential of particles. SLN formulations were optimized using Box-Behnken design. The particles were freeze dried and morphologically studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The in-vitro release profile of propolis entrapped in the optimized nanoparticles was investigated. Results: The mean particle size, PDI, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency (EE) and loading efficiency (LE) of optimized propolis-loaded SLNs were found to be 122.6±22.36 nm, 0.28±0.06, -26.18±3.3 mV, 73.57±0.86% and 3.29±0.27%, respectively. SEM images exhibited nanoparticles to be non-aggregated and in spherical shape. The in-vitro release study showed prolonged release of propolis from nanoparticles. Conclusion: The results implied that the proposed way of SLN preparation could be considered as a proper method for production of propolis loaded colloidal carrier system.
Keywords: Box-Behnken design; Drug delivery; Propolis; Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN); Solvent emulsification-evaporation method.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Yuan J, Lu Y, Abula S, Hu Y, Liu J, Fan Y. et al. Optimization on preparation condition of propolis flavonoids liposome by response surface methodology and research of its immunoenhancement activity. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:505703. doi: 10.1155/2013/505703. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orsi RO, Funari SRC, Soares AM, Calvi SA, Oliveira SL, Sforcin JM. et al. Immunomodulatory action of propolis on macrophage activation. J Venom Anim Toxins. 2000;6(2):205–19. doi: 10.1590/s0104-79302000000200006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources