In Vitro Anti-cancer Activity of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increased after Infection with Oncolytic Reovirus
- PMID: 33880359
- PMCID: PMC8046384
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2021.034
In Vitro Anti-cancer Activity of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increased after Infection with Oncolytic Reovirus
Abstract
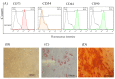
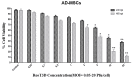
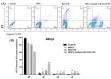
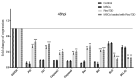
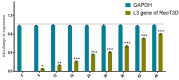
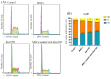
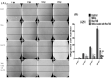
Purpose: Reovirus type 3 Dearing (ReoT3D), a wild type oncolytic virus (OV) from the Reoviridae family, kills KRAS mutant cancer cells. However, the use of OVs has faced with some limitations such as immune responses, and delivery of OVs to the tumor sites in systemic therapy. To solve this, and also to increase the anti-cancer effects of these OVs, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) might be used as an effective vehicle for OVs delivery. In this study, we examined the anti-cancer effects of human adipose derived-MSCs (AD-MSCs) as a vehicle of ReoT3D against human glioblastoma cells. Methods: Here, AD-MSCs were characterized and toxicity of ReoT3D on them was determined by 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Then, capability of AD-MSCs for virus production was assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and different in vitro anti-cancer experiments were applied for our anti-cancer purposes. Results: Our results from toxicity assay revealed that the isolated and provoked AD-MSCs were resistant to nontoxic concentration multiplicity of infection (MOI) >1 pfu/cells of ReoT3D. In addition, the results indicated that AD-MSCs were susceptible for virus life cycle complementation and were capable for production of virus progenies. Furthermore, our results showed that AD-MSCs had oncolysis effects and increased the anti-cancer effects of ReoT3D. Conclusion: AD-MSCs as a susceptible host for oncolytic reovirus could increase the anti-cancer activity of this OV against glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cell line.
Keywords: Glioblastoma cancer; Mesenchymal stem cell; Oncolytic virus; Reovirus type 3 Dearing.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous