The Beneficial Effects of Actinomycetales Immune Modulators in the Pancreas of Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 33880360
- PMCID: PMC8046390
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2021.035
The Beneficial Effects of Actinomycetales Immune Modulators in the Pancreas of Diabetic Rats
Abstract
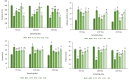
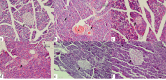
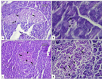
Purpose: Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) has dramatically increased in recent years, especially in young people, and limits the life quality of the patients involved. Thus, many researchers are performing extensive studies to find alternative treatments for DM. Methods: Here, we evaluated the improvement effects of the heat-killed Actinomycetales species, including Gordonia bronchialis, and Tsukamurella inchonensis in streptozotocin (STZ)- diabetic rats by biochemical, immunological, and histopathological examinations. Results: The present findings exhibited a dramatic and progressive alteration in the serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the diabetic group, which were related to the blood glucose and insulin levels, oxidative stress defense (evaluated by TAC and MDA activities), and the pancreas biochemical indicators (such as amylase and lipase). More importantly, the present results were consistent with the histopathological findings, which included cellular degeneration, vascular congestion, hemorrhage, focal necrosis associated with mononuclear cell infiltration. Interestingly, all of the diabetic changes in the blood serum and tissues improved remarkably in the treated groups by Actinomycetales species. Conclusion: Surprisingly, most of the current diabetic complications effectively attenuated after oral administration of both Actinomycetales species, particularly with a high dose of T. inchonensis. Thus, it is concluded that the heat-killed Actinomycetales species can prevent and improve the progression of T1DM and its various complications profoundly.
Keywords: Biochemical indicators; Diabetes mellitus; Histopathology; Immunotherapy; Inflammatory cytokines.
© 2021 The Authors.
Similar articles
-
Beneficial effects of immunotherapy with extracts derived from Actinomycetales on rats with spontaneous obesity and diabetes.Immunotherapy. 2012 May;4(5):487-97. doi: 10.2217/imt.12.37. Immunotherapy. 2012. PMID: 22642332
-
Elevation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6 levels in aortic intima of Chinese Guizhou minipigs with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Chin Med J (Engl). 2007 Mar 20;120(6):479-84. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007. PMID: 17439741
-
Antidiabetic effect of total flavonoids from Sanguis draxonis in type 2 diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Oct 7;149(3):729-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.07.035. Epub 2013 Aug 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23933499
-
Allium hookeri root protects oxidative stress-induced inflammatory responses and β-cell damage in pancreas of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Feb 17;16:63. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1032-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 26888412 Free PMC article.
-
Withaferin-A attenuates multiple low doses of Streptozotocin (MLD-STZ) induced type 1 diabetes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:1428-1440. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.090. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30119216
Cited by
-
Immuno-modulatory Effects of Inactivated Dietzia Maris on the Selected Aspects of Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses in Mice.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Jul 20;12:183. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_121_22. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37694256 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources