Liraglutide Regulates the Kidney and Liver in Diabetic Nephropathy Rats through the miR-34a/SIRT1 Pathway
- PMID: 33880382
- PMCID: PMC8046563
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8873956
Liraglutide Regulates the Kidney and Liver in Diabetic Nephropathy Rats through the miR-34a/SIRT1 Pathway
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the regulatory effects of liraglutide on the kidney and liver through the miR-34a/SIRT1 pathway with related factors in diabetic nephropathy (DN) rats.
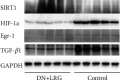
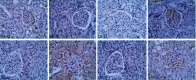
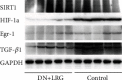
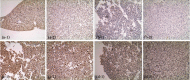
Methods: DN rats were randomly divided into two groups (n = 10) and were injected with liraglutide or normal saline twice a day. The 24-hour urine microalbumin content and biochemical index levels were measured. qRT-PCR was performed to detect the expression of miR-34a in the kidney and liver tissues. The levels of SIRT1, HIF-1a, Egr-1, and TGF-β1 in kidney and liver tissues were determined using qRT-PCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry. Electron microscopy and HE staining were used to observe the ultrastructure and pathological changes.
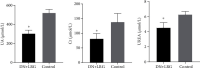
Results: Liraglutide treatment in DN rats decreased blood glucose, 24-hour urine microalbumin, TC, TG, LDL-C, UA, Cr, UREA, ALT, and AST levels and increased the level of HDL-C (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the miR-34a levels were significantly decreased in kidney and liver tissues followed by liraglutide treatment (P < 0.05). The levels of SIRT1 in the liraglutide group are significantly higher than those in the control group with the kidney and liver tissues (P < 0.05). Conversely, the contents of HIF-1a, Egr-1, and TGF-β1 were significantly lower in the liraglutide group than in the control group (P < 0.05). Electron microscopy showed that the kidney of the liraglutide-treated group exhibited minor broadening of the mesangial areas, fewer deposits, and a well-organized foot process. HE staining revealed that the kidney of the liraglutide-treated rats had a more regular morphology of the glomerulus and Bowman sac cavity and lighter tubular edema. Additionally, the liraglutide-treated DN rats had a clear hepatic structure, a lower degree of steatosis, and mild inflammatory cell infiltration.
Conclusion: Liraglutide, through its effect on the miR-34a/SIRT1 pathway, may have a protective role in the kidney and liver of DN rats.
Copyright © 2021 Shan Xiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




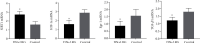





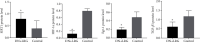

References
-
- Callcott E. T., Santhakumar A. B., Luo J., Blanchard C. L. Therapeutic potential of rice-derived polyphenols on obesity-related oxidative stress and inflammation. Journal of Applied Biomedicine. 2018;16(4):255–262. doi: 10.1016/j.jab.2018.03.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

