Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and virologic features of COVID-19 patients in Kazakhstan: A nation-wide retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 33880458
- PMCID: PMC8050615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100096
Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and virologic features of COVID-19 patients in Kazakhstan: A nation-wide retrospective cohort study
Abstract
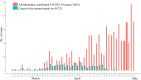
Background: The earliest coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) cases in Central Asia were announced in March 2020 by Kazakhstan. Despite the implementation of aggressive measures to curb infection spread, gaps remain in the understanding of the clinical and epidemiologic features of the regional pandemic.
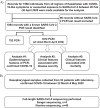
Methods: We did a retrospective, observational cohort study of patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 hospitalized in Kazakhstan between February and April 2020. We compared demographic, clinical, laboratory and radiological data of patients with different COVID-19 severities on admission. Logistic regression was used to assess factors associated with disease severity and in-hospital death. Whole-genome SARS-CoV-2 analysis was performed in 53 patients.
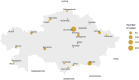
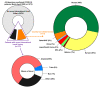
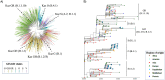
Findings: Of the 1072 patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in March-April 2020, the median age was 36 years (IQR 24-50) and 484 (45%) were male. On admission, 683 (64%) participants had asymptomatic/mild, 341 (32%) moderate, and 47 (4%) severe-to-critical COVID-19 manifestation; 20 in-hospital deaths (1•87%) were reported by 5 May 2020. Multivariable regression indicated increasing odds of severe disease associated with older age (odds ratio 1•05, 95% CI 1•03-1•07, per year increase; p<0•001), the presence of comorbidities (2•34, 95% CI 1•18-4•85; p=0•017) and elevated white blood cell count (WBC, 1•13, 95% CI 1•00-1•27; p=0•044) on admission, while older age (1•09, 95% CI 1•06-1•13, per year increase; p<0•001) and male sex (5•63, 95% CI 2•06-17•57; p=0•001) were associated with increased odds of in-hospital death. The SARS-CoV-2 isolates grouped into seven phylogenetic lineages, O/B.4.1, S/A.2, S/B.1.1, G/B.1, GH/B.1.255, GH/B.1.3 and GR/B.1.1.10; 87% of the isolates were O and S sub-types descending from early Asian lineages, while the G, GH and GR isolates were related to lineages from Europe and the Americas.
Interpretation: Older age, comorbidities, increased WBC count, and male sex were risk factors for COVID-19 disease severity and mortality in Kazakhstan. The broad SARS-CoV-2 diversity suggests multiple importations and community-level amplification predating travel restriction.
Funding: Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Keywords: COVID-19; Central Asia; Clinical characteristics; Disease risk factors; Disease severity; Kazakhstan; Molecular epidemiology; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2 genomics.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality predictors of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: Retrospective cohort study from Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 22;16(12):e0261272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261272. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34936681 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome by SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Other Etiologic Agents Among Brazilian Indigenous Population: An Observational Study from the First Year of Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19 Pandemic.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022 Apr;8:100177. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100177. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022. PMID: 35018359 Free PMC article.
-
Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes of 27,256 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Kermanshah Province, Iran: a retrospective one-year cohort study.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Mar 31;22(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07312-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35361161 Free PMC article.
-
Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections and prediction of moderate-to-severe outcomes during rituximab therapy in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in the UK: a single-centre cohort study.Lancet Rheumatol. 2023 Feb;5(2):e88-e98. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00004-8. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36712951 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory Features of Hospitalised Patients with COVID-19 in Jersey, UK.EJIFCC. 2022 Aug 8;33(2):105-120. eCollection 2022 Aug. EJIFCC. 2022. PMID: 36313915 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in Karaganda, Kazakhstan before the launch of COVID-19 vaccination.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 27;17(7):e0272008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272008. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35895743 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality predictors of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: Retrospective cohort study from Nur-Sultan, Kazakhstan.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 22;16(12):e0261272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261272. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34936681 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Gam-COVID-Vac, an Adv5/Adv26 COVID-19 vaccine, on the biomarkers of endothelial function, coagulation and platelet activation.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 18;18(10):e0293074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293074. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37851684 Free PMC article.
-
Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes in hospitalized patients during six waves of COVID‑19 in Northern Iran: a large cohort study.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 18;13(1):22527. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50139-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38110656 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of viral pathogens associated with symptomatic upper respiratory tract infection in adults during a low COVID-19 transmission period.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 13;11:e15008. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15008. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36935913 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

