H3K14 hyperacetylation‑mediated c‑Myc binding to the miR‑30a‑5p gene promoter under hypoxia postconditioning protects senescent cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
- PMID: 33880587
- PMCID: PMC8097758
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12107
H3K14 hyperacetylation‑mediated c‑Myc binding to the miR‑30a‑5p gene promoter under hypoxia postconditioning protects senescent cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
Abstract
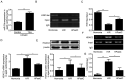
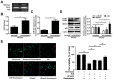
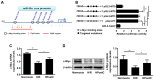
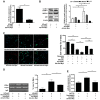
Our previous study reported that microRNA (miR)‑30a‑5p upregulation under hypoxia postconditioning (HPostC) exert a protective effect on aged H9C2 cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via DNA methyltransferase 3B‑induced DNA hypomethylation at the miR‑30a‑5p gene promoter. This suggests that miR‑30a‑5p may be a potential preventative and therapeutic target for ischemic heart disease in aged myocardium. The present study aimed to investigate the underlying mechanisms of miR‑30a‑5p transcription in aged myocardium in ischemic heart disease. Cardiomyocytes were treated with 8 mg/ml D‑galactose for 9 days, and then exposed to hypoxic conditions. Cell viability was determined using a cell viability assay. Expression levels of histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2), LC3B‑II/I, beclin‑1 and p62 were detected via reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR and western blotting. Chromatin immunoprecipitation‑PCR and luciferase reporter assays were performed to evaluate the effect of c‑Myc binding and activity on the miR‑30a‑5p promoter in senescent cardiomyocytes following HPostC. It was found that HPostC enhanced the acetylation levels of H3K14 at the miR‑30a‑5p gene promoter in senescent cardiomyocytes, which attributed to the decreased expression of HDAC2. In addition, c‑Myc could positively regulate miR‑30a‑5p transcription to inhibit senescent cardiomyocyte autophagy. Mechanically, it was observed that increased H3K14 acetylation level exposed to romidepsin facilitated c‑Myc binding to the miR‑30a‑5p gene promoter region, which led to the increased transcription of miR‑30a‑5p. Taken together, these results demonstrated that HDAC2‑mediated H3K14 hyperacetylation promoted c‑Myc binding to the miR‑30a‑5p gene promoter, which contributed to HPostC senescent cardioprotection.
Keywords: autophagy; c‑Myc; hypoxia postconditioning; hypoxia/reoxygenation; histone acetylation; microrna‑30a‑5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA Hypomethylation of miR-30a Mediated the Protection of Hypoxia Postconditioning Against Aged Cardiomyocytes Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury Through Inhibiting Autophagy.Circ J. 2020 Mar 25;84(4):616-625. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-19-0915. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Circ J. 2020. PMID: 32115441
-
miR‑30a‑5p mitigates autophagy by regulating the Beclin‑1/ATG16 pathway in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Jul;48(1):144. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4977. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34080645 Free PMC article.
-
The lncRNA, H19 Mediates the Protective Effect of Hypoxia Postconditioning Against Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Injury to Senescent Cardiomyocytes by Targeting microRNA-29b-3p.Shock. 2019 Aug;52(2):249-256. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001213. Shock. 2019. PMID: 29958242
-
Positive feedback loop of lncRNA SNHG1/miR‑16‑5p/GATA4 in the regulation of hypoxia/reoxygenation‑induced cardiomyocyte injury.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Jan;25(1):28. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12544. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 34841440 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic Postconditioning Protects against Aged Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation of miR-181a-2-3p.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 24;2022:9635674. doi: 10.1155/2022/9635674. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35656020 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
2-aminoethoxydiphenylborane intervenes intracellular calcium signaling and attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice through ITPR1/MCU pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 12;15(1):29469. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14822-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40797070 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of histone acetylation sites in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 15;10:1133611. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1133611. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37008337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptosporidium parvum regulates HCT-8 cell autophagy to facilitate survival via inhibiting miR-26a and promoting miR-30a expression.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Dec 15;15(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05606-y. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36522638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhmedov A, Montecucco F, Costantino S, Vdovenko D, Schaub Clerigué A, Gaul DS, Burger F, Roth A, Carbone F, Liberale L, et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific JunD overexpression increases infarct size following ischemia/reperfusion cardiac injury by downregulating Sirt3. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:168–180. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3400299. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

