eNose-TB: A trial study protocol of electronic nose for tuberculosis screening in Indonesia
- PMID: 33882070
- PMCID: PMC8059810
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249689
eNose-TB: A trial study protocol of electronic nose for tuberculosis screening in Indonesia
Abstract
Background: Even though conceptually, Tuberculosis (TB) is almost always curable, it is currently the world's leading infectious killer. Patients with pulmonary TB are the source of transmission. Approximately 23% of the world's population is believed to be latently infected with TB bacteria, and 5-15% of them will progress at any point in time to develop the disease. There was a global diagnostic gap of 2.9 million between notifications of new cases and the estimated number of incident cases, and Indonesia carries the third-highest of this gap. Therefore, screening TB among the community is of great importance to prevent further transmission and infection. The electronic nose for screening TB (eNose-TB) project is initiated in Yogyakarta, Indonesia, to screen TB by breath test with an electronic-nose that is easy-to-use, point-of-care, does not expose patients to radiation, and can be produced at low cost.
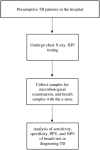
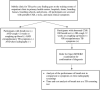
Methods/design: The objectives of the two-phase planned project are to: 1) investigate the potential of an eNose-TB as a screening tool in Indonesia, in comparison with screening with clinical symptoms and chest radiology, which are currently used as a standard, and 2) analyze the time and cost of a screening algorithm with eNose-TB to obtain additional case detection. A cross-sectional study will be conducted in the first phase to validate the eNose-TB. The validation phase will involve 395 presumptive TB patients in the Surakarta General Hospital, Central Java. In the second phase, a cross-sectional research will be conducted, involving 1,383 adults and children in the municipality of Yogyakarta and Kulon Progo district of Yogyakarta Province.
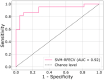
Discussion: The findings will provide data concerning the sensitivity and specificity of the eNose-TB as a screening tool for tuberculosis, and the time and cost analysis of a screening algorithm with the eNose.
Trial registration: NCT04567498; https://clinicaltrials.gov/.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. Geneva; 2020. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/.
-
- Riono P. TB Elimination in Indonesia. 2018 [cited 13 Nov 2018]. http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/info-terkini/materiprarakerke....
-
- World Health Organization. Systematic screening for active tuberculosis. 2015; 146. ISBN 978 92 4 154860 1.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

