Current progress and quality of radiomic studies for predicting EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using PET/CT images: a systematic review
- PMID: 33882244
- PMCID: PMC8173688
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20201272
Current progress and quality of radiomic studies for predicting EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using PET/CT images: a systematic review
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the methodological quality of radiomic studies based on positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) images predicting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
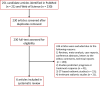
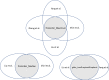
Methods: We systematically searched for eligible studies in the PubMed and Web of Science datasets using the terms "radiomics", "PET/CT", "NSCLC", and "EGFR". The included studies were screened by two reviewers independently. The quality of the radiomic workflow of studies was assessed using the Radiomics Quality Score (RQS). Interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to determine inter rater agreement for the RQS. An overview of the methodologies used in steps of the radiomics workflow and current results are presented.
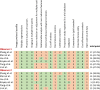
Results: Six studies were included with sample sizes of 973 ranging from 115 to 248 patients. Methodologies in the radiomic workflow varied greatly. The first-order statistics were the most reproducible features. The RQS scores varied from 13.9 to 47.2%. All studies were scored below 50% due to defects on multiple segmentations, phantom study on all scanners, imaging at multiple time points, cut-off analyses, calibration statistics, prospective study, potential clinical utility, and cost-effectiveness analysis. The ICC results for majority of RQS items were excellent. The ICC for summed RQS was 0.986 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.898-0.998].
Conclusions: The PET/CT-based radiomics signature could serve as a diagnostic indicator of EGFR mutation status in NSCLC patients. However, the current conclusions should be interpreted with care due to the suboptimal quality of the studies. Consensus for standardization of PET/CT-based radiomic workflow for EGFR mutation status in NSCLC patients is warranted to further improve research.
Advances in knowledge: Radiomics can offer clinicians better insight into the prediction of EGFR mutation status in NSCLC patients, whereas the quality of relative studies should be improved before application to the clinical setting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment of CT Radiomics-Based Models Predicting Tumor EGFR Mutation Status in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11433. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411433. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511192 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Radiogenomics Sequencing for Prediction of EGFR and KRAS Mutation Status in NSCLC Patients Using Multimodal Imaging and Machine Learning Algorithms.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Aug;22(4):1132-1148. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01487-8. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 32185618
-
Value of pre-therapy 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics in predicting EGFR mutation status in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 May;47(5):1137-1146. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04592-1. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31728587
-
Impact of feature harmonization on radiogenomics analysis: Prediction of EGFR and KRAS mutations from non-small cell lung cancer PET/CT images.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Mar;142:105230. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105230. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35051856
-
Post-radiotherapy stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer radiomics research: a systematic review and comparison of CLEAR and RQS frameworks.Eur Radiol. 2024 Oct;34(10):6527-6543. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10736-1. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38625613 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment of CT Radiomics-Based Models Predicting Tumor EGFR Mutation Status in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 14;24(14):11433. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411433. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511192 Free PMC article.
-
Recent and current advances in PET/CT imaging in the field of predicting epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 6;12:879341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879341. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review of the radiomics quality score applications: an EuSoMII Radiomics Auditing Group Initiative.Eur Radiol. 2023 Mar;33(3):1884-1894. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09187-3. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36282312 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Prediction of Molecular Tumor Biomarkers from H&E: A Practical Review.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 7;12(12):2022. doi: 10.3390/jpm12122022. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36556243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New PET/CT criterion for predicting lymph node metastasis in resectable advanced (stage IB-III) lung cancer: The standard uptake values ratio of ipsilateral/contralateral hilar nodes.Thorac Cancer. 2022 Mar;13(5):708-715. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14302. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35048499 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous