Novel RT-ddPCR assays for measuring the levels of subgenomic and genomic SARS-CoV-2 transcripts
- PMID: 33882362
- PMCID: PMC8105137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.04.011
Novel RT-ddPCR assays for measuring the levels of subgenomic and genomic SARS-CoV-2 transcripts
Abstract
The replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses depends on transcription of negative-sense RNA intermediates that serve as the templates for the synthesis of positive-sense genomic RNA (gRNA) and multiple different subgenomic mRNAs (sgRNAs) encompassing fragments arising from discontinuous transcription. Recent studies have aimed to characterize the expression of subgenomic SARS-CoV-2 transcripts in order to investigate their clinical significance. Here, we describe a novel panel of reverse transcription droplet digital PCR (RT-ddPCR) assays designed to specifically quantify multiple different subgenomic SARS-CoV-2 transcripts and distinguish them from transcripts that do not arise from discontinuous transcription at each locus. These assays can be applied to samples from SARS-CoV-2 infected patients to better understand the regulation of SARS-CoV-2 transcription and how different sgRNAs may contribute to viral pathogenesis and clinical disease severity.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Digital PCR; Droplet digital PCR; Quantitative assays; SARS-CoV-2; Subgenomic RNA; Viral transcription/replication.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


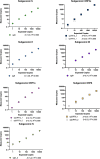

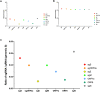
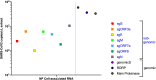



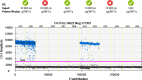
References
-
- Sawicki S.G., Sawicki D.L. Coronaviruses use discontinuous extension for synthesis of subgenome-length negative strands. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;380:499–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

