Use of circular RNAs as markers of readthrough transcription to identify factors regulating cleavage/polyadenylation events
- PMID: 33882363
- PMCID: PMC8522170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.04.012
Use of circular RNAs as markers of readthrough transcription to identify factors regulating cleavage/polyadenylation events
Abstract
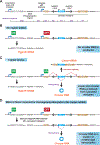
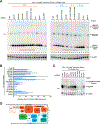
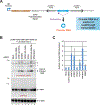
Circular RNAs with covalently linked ends are generated from many eukaryotic protein-coding genes when the pre-mRNA splicing machinery backsplices. These mature transcripts are resistant to digestion by exonucleases and typically have much longer half-lives than their associated linear mRNAs. Circular RNAs thus have great promise as sensitive biomarkers, including for detection of transcriptional activity. Here, we show that circular RNAs can serve as markers of readthrough transcription events in Drosophila and human cells, thereby revealing mechanistic insights into RNA polymerase II transcription termination as well as pre-mRNA 3' end processing. We describe methods that take advantage of plasmids that generate a circular RNA when an upstream polyadenylation signal fails to be used and/or RNA polymerase II fails to terminate. As a proof-of-principle, we show that RNAi-mediated depletion of well-established transcription termination factors, including the RNA endonuclease Cpsf73, results in increased circular RNA output from these plasmids in Drosophila and human cells. This method is generalizable as a circular RNA can be easily encoded downstream of any genomic region of interest. Circular RNA biomarkers, therefore, have great promise for identifying novel cellular factors and conditions that impact transcription termination processes.
Keywords: Backsplicing; Cpsf73; RNAi screening; Transcription termination; circRNA; pre-mRNA 3′ end processing.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J, The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs, Nat Rev Genet 20(11) (2019) 675–691. - PubMed
-
- Chen LL, The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(8) (2020) 475–490. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Xue W, Li X, Zhang J, Chen S, Zhang JL, Yang L, Chen LL, The Biogenesis of Nascent Circular RNAs, Cell Rep 15(3) (2016) 611–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

